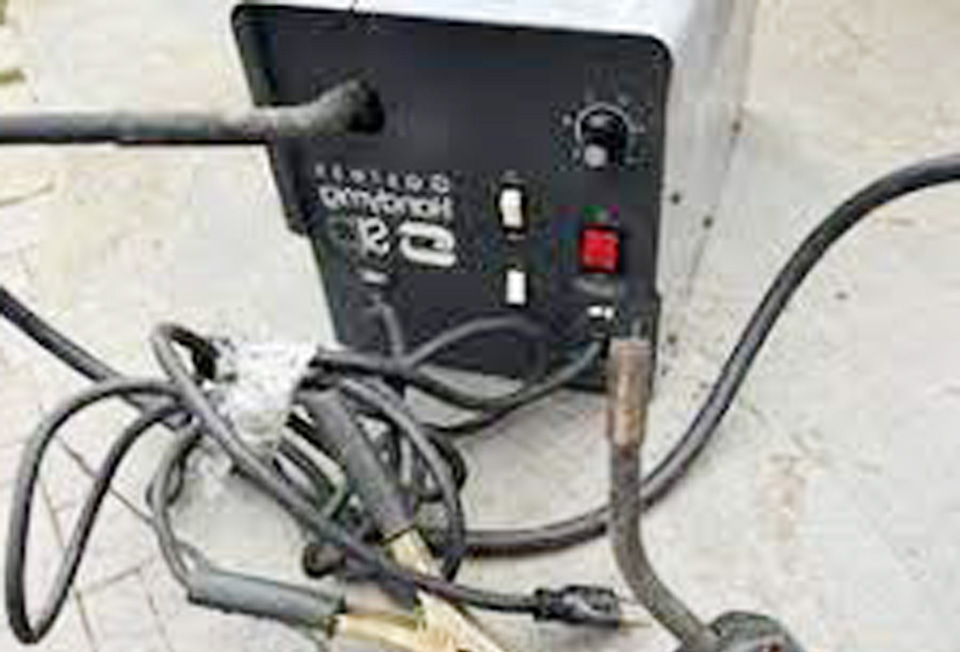
Welding transformers are essential components in the world of welding, providing the necessary power and current control for various welding applications. These devices have been a cornerstone of welding technology for nearly a century, offering reliability and simplicity in welding operations.
We’ll explore the nature, function, advantages, and limitations of welding transformers, as well as their place in modern welding practices.

Image by reddit
Understanding Welding Transformers
A welding transformer is an electrical device designed to convert standard AC power from a wall outlet into a lower voltage, higher current output suitable for welding. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, using two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core to step down the voltage and increase the current.
Key Components of a Welding Transformer:
- Primary Coil: Connected to the power source, typically 120V or 240V AC.
- Secondary Coil: Produces the lower voltage, higher current output for welding.
- Iron Core: Facilitates the magnetic field transfer between coils.
- Taps or Switches: Allow for adjusting the output current.
How Welding Transformers Work
When AC power is applied to the primary coil, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field in the iron core. This magnetic field then induces a current in the secondary coil. The ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils determines the voltage step-down and current increase.
For example, if the primary coil has 1000 turns and the secondary has 100 turns, the voltage will be reduced by a factor of 10, while the current will increase by the same factor. This transformation is crucial for welding, as it provides the high current necessary to melt metal while maintaining a safer, lower voltage.
Advantages of Welding Transformers
Reliability
Transformer welding machines are known for their durability and long lifespan. With fewer complex components, they are less prone to failure compared to more modern inverter-based machines.
Simplicity
The straightforward design makes transformer welders easy to operate and maintain, making them ideal for novice welders or those who prefer uncomplicated equipment.
Cost-Effective
Generally, transformer welders are less expensive than their inverter counterparts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers or those who weld infrequently.
Robust Performance
Transformer welders can handle harsh environments and are less sensitive to power fluctuations, making them suitable for outdoor use or when connected to generators.
Suitable for Heavy-Duty Welding
Their ability to produce high currents consistently makes them excellent for thick material welding and heavy-duty applications.
Limitations of Welding Transformers
Size and Weight
One of the most significant drawbacks of transformer welders is their bulkiness. The large transformer core makes these machines heavy and less portable compared to inverter welders.
Energy Efficiency
Transformer welders are generally less energy-efficient than inverter models. They consume more power and may lead to higher electricity costs over time.
Limited Control
While they provide reliable welding current, transformer welders offer less precise control over welding parameters compared to modern inverter-based machines.
AC Output
Most basic transformer welders produce AC output, which can be less stable for certain welding processes or materials compared to DC output.
Limited Versatility
Transformer welders are typically designed for specific welding processes (e.g., stick welding) and may not offer the multi-process capabilities of inverter machines.
Applications of Welding Transformers
Welding transformers are widely used in various applications, including:
- Construction: For structural steel welding and repairs.
- Automotive Industry: In body shops and repair facilities.
- Agriculture: For equipment repair and maintenance.
- DIY and Home Projects: Popular among hobbyists for their simplicity and reliability.
- Industrial Maintenance: In factories and plants for repair work.
Welding Processes Supported
While primarily associated with stick welding (SMAW – Shielded Metal Arc Welding), some transformer welders can also support:
TIG Welding (GTAW): With additional components for AC TIG welding.
MIG Welding (GMAW): Some models can be adapted for basic MIG welding.
Choosing a Welding Transformer
When selecting a welding transformer, consider the following factors:
- Power Requirements: Ensure the transformer can handle your typical welding tasks in terms of amperage output and duty cycle.
- Input Voltage: Choose between 120V for lighter work or 240V for more powerful applications.
- Portability Needs: If you need to move the welder frequently, consider the weight and size limitations.
- Welding Processes: Determine which welding processes you need to perform and choose a machine that supports them.
- Duty Cycle: For continuous or heavy-duty welding, look for machines with higher duty cycles.
- Budget: Balance the initial cost with long-term operational expenses.
Maintenance and Care
To ensure the longevity and performance of your welding transformer:
- Keep it clean and dry, protecting it from dust and moisture.
- Regularly inspect and tighten electrical connections.
- Check and replace worn cables or connectors.
- Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and recommendations.
Future of Welding Transformers
While inverter technology has become increasingly popular in recent years, welding transformers continue to hold a significant place in the welding industry. Their reliability, simplicity, and suitability for certain applications ensure their ongoing relevance.
However, as energy efficiency and advanced control features become more critical, transformer technology in welding is evolving. Some manufacturers are developing hybrid systems that combine the reliability of transformers with the efficiency and control of inverter technology.
Conclusion
Welding transformers remain a vital tool in the welding industry, offering reliability, simplicity, and robust performance. While they may lack some of the advanced features of modern inverter welders, their strengths in durability and straightforward operation make them an excellent choice for many welding applications.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of welding transformers allows welders to make informed decisions about their equipment choices. Whether you’re a professional welder, a DIY enthusiast, or somewhere in between, a welding transformer might be the right tool for your welding needs.
As welding technology continues to advance, welding transformers will likely evolve, potentially incorporating new features while maintaining their core strengths. For now, they remain a trusted and valuable option in the diverse world of welding equipmen

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.