Are you a beginner looking to get started with TIG welding? In this article, we will walk you through the basics of TIG welding, giving you a solid foundation to build upon. TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is known for its versatility and precision, making it a popular choice among professionals and hobbyists alike. Whether you’re interested in creating intricate designs or repairing metal objects, TIG welding can help you achieve clean and durable welds.

Photo by dsportmag
What is TIG welding?
TIG welding is a welding process that uses a tungsten electrode to create an arc between the electrode and the workpiece. Unlike other welding processes, TIG welding does not require a consumable filler material, making it ideal for projects that require high-quality welds. The arc generated by the electrode heats the workpiece and melts the base metal, creating a pool of molten metal that solidifies to form a strong bond.
TIG welding is commonly used for welding stainless steel, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals. It is particularly well-suited for applications that require precise control over the welding process, such as thin materials, intricate designs, or welding in tight spaces. TIG welding offers excellent weld appearance, minimal distortion, and strong, durable welds.
Advantages of TIG welding
TIG welding offers several advantages over other welding processes. One of the key advantages is its ability to produce high-quality welds with minimal spatter. This is especially important when working with materials that require a clean and aesthetic finish, such as stainless steel or aluminum. The precise control over the welding process also allows for greater weld accuracy, making TIG welding suitable for intricate designs and detailed work.
Another advantage of TIG welding is its versatility. It can be used to weld a wide range of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals. This makes it a valuable skill for welders working in various industries, from automotive and aerospace to art and sculpture. TIG welding can be performed in all positions, making it adaptable to different welding scenarios.
TIG welding equipment and materials
To get started with TIG welding, you will need a few essential pieces of equipment and materials. The primary equipment is a TIG welder, which consists of a power source, a welding torch, and a foot pedal or hand control for adjusting the welding current. TIG welders come in various sizes and power outputs, so choose one that suits your needs and budget.
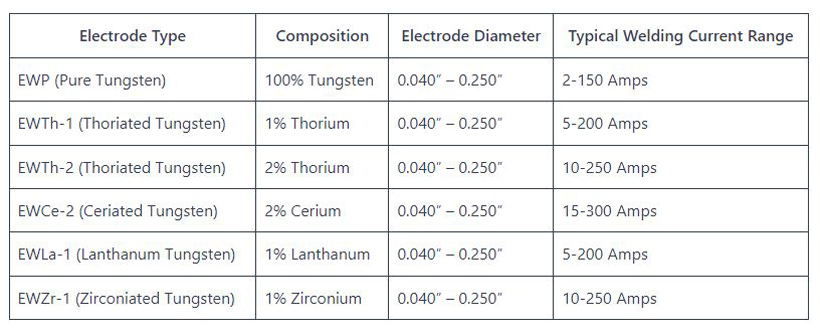
In addition to the TIG welder, you will also need a tungsten electrode, which is the key component that creates the arc in TIG welding. Tungsten electrodes are available in different compositions and sizes, so it’s important to select the right electrode for the material you’ll be welding. Other materials you will need include filler rods, shielding gas, and protective gear such as welding gloves, helmet, and safety glasses.
Setting up your TIG welding workstation is crucial for a successful welding experience. The welding area should be clean, well-ventilated, and free from flammable materials. Make sure you have a sturdy worktable or welding bench, as well as a reliable power source. Proper grounding is also essential to ensure electrical safety and prevent damage to your welding equipment.
TIG welding techniques
TIG welding involves several techniques that allow you to control the welding process and produce high-quality welds. The first technique is called “scratch start,” where you touch the tungsten electrode to the workpiece to initiate the arc. This technique is commonly used for manual TIG welding and is suitable for welding thicker materials.
Another technique is called “lift start,” where you hold the tungsten electrode just above the workpiece and slowly lower it until the arc ignites. This technique is useful when working with thin materials or when you want to avoid scratching the surface of the workpiece. Lift start is also commonly used for TIG welding aluminum.
Once the arc is established, you can begin welding by manipulating the welding torch and filler rod. The key to successful TIG welding is maintaining a stable arc length and controlling the welding speed. It’s important to practice proper torch and hand positioning to achieve consistent welds. Remember to move the torch along the joint in a smooth and steady motion, maintaining a consistent travel speed.
Safety precautions for TIG welding
As with any welding process, TIG welding requires strict adherence to safety precautions to protect yourself and others from potential hazards. The first and most crucial safety measure is to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes welding gloves, a welding helmet with a proper shade, and safety glasses with side shields to protect your eyes from harmful UV radiation.
Ensure that your work area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of toxic fumes and gases. If you’re working indoors, consider using ventilation fans or exhaust systems to remove welding fumes. It’s also important to be aware of fire hazards and keep a fire extinguisher nearby in case of emergencies. Before starting any welding project, inspect your equipment for any damage or defects, and ensure that all connections are secure.
TIG welding tips for beginners
As a beginner, there are a few tips and tricks that can help you improve your TIG welding skills. First and foremost, practice is key. Take the time to practice on scrap pieces of metal before attempting any important projects. This will allow you to get a feel for the welding process and make adjustments as needed.
Pay attention to your tungsten electrode. It’s important to keep the electrode clean and sharp to ensure a stable arc and minimize contamination of the weld. You can sharpen the electrode using a dedicated tungsten electrode grinder or a bench grinder. Remember to grind the electrode in the direction of the grain to maintain a consistent point.
Controlling the heat input is crucial in TIG welding. Heat control can be achieved by adjusting the welding current, travel speed, and torch angle. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance between penetration and heat input for your specific welding application.
Common TIG welding mistakes to avoid
Even experienced welders make mistakes, but being aware of common TIG welding mistakes can help you avoid them. One common mistake is improper tungsten electrode preparation. Make sure to clean the electrode thoroughly and remove any contaminants before starting a weld. Contaminated electrodes can cause unstable arcs and lead to poor weld quality.
Another mistake is improper shielding gas coverage. Shielding gas is essential to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. Ensure that the gas flow rate is set correctly and that the gas nozzle is positioned close enough to the weld joint to provide adequate shielding. Insufficient shielding can result in weld defects such as porosity or oxidation.
TIG welding projects for beginners
Once you have mastered the basics of TIG welding, you can start exploring various projects to hone your skills. A simple project for beginners is welding two pieces of metal together to form a T-joint or a lap joint. This will allow you to practice maintaining a consistent arc length and controlling the welding speed.
As you gain more experience, you can move on to more complex projects such as welding aluminum or stainless steel sculptures, repairing metal furniture, or creating custom metal artwork. The possibilities are endless, and TIG welding opens up a world of creativity and craftsmanship.
TIG welding certifications and training programs
If you’re serious about pursuing a career in welding or want to enhance your skills, you may consider obtaining TIG welding certifications or enrolling in training programs. TIG welding certifications are recognized credentials that demonstrate your proficiency in TIG welding. They can greatly enhance your job prospects and open doors to higher-paying welding positions.
Many vocational schools, community colleges, and trade organizations offer TIG welding training programs. These programs provide hands-on training, theoretical knowledge, and practical experience to help you become a skilled TIG welder. Some welding equipment manufacturers offer workshops and seminars to help welders improve their skills and familiarize themselves with the latest welding technologies.
Conclusion
TIG welding is a versatile and precise welding process that offers clean and durable welds. By understanding the basics of TIG welding, having the right equipment and materials, and following proper safety precautions, you can embark on your welding journey with confidence.
To practice regularly, learn from your mistakes, and never stop exploring new projects and techniques. With dedication and perseverance, you can become a skilled TIG welder capable of tackling a wide range of welding applications.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.