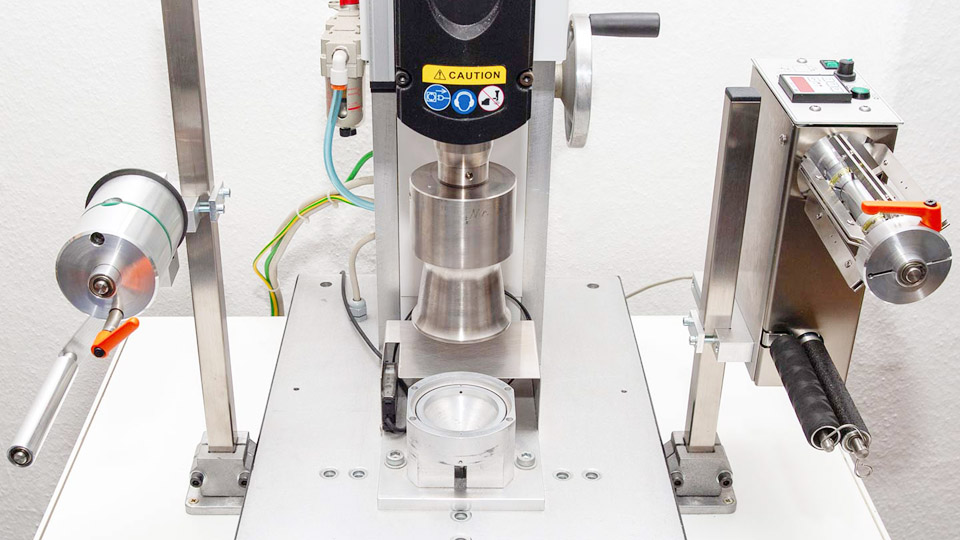
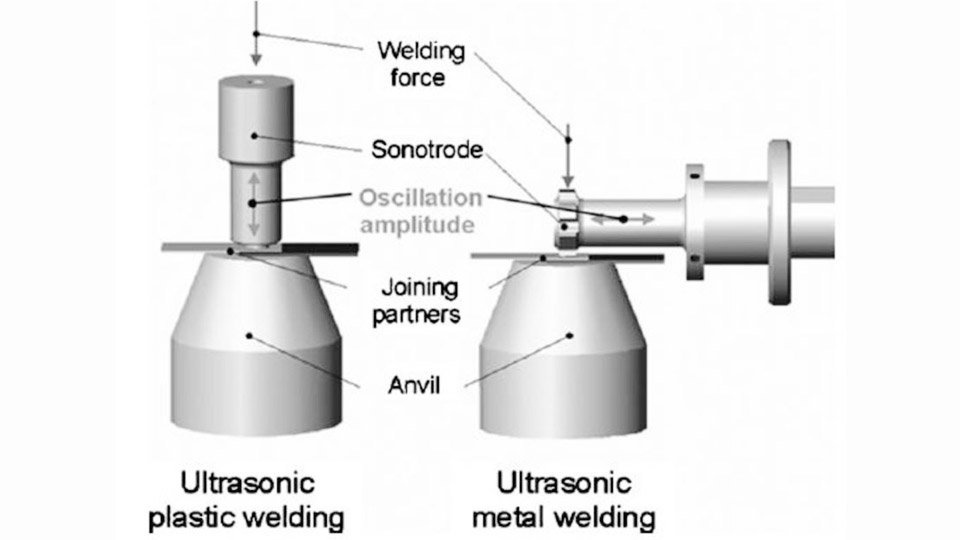
Ultrasonic welding is a versatile and efficient joining process that has found widespread use across various industries. This innovative technique uses high-frequency vibrations to create strong bonds between materials, particularly thermoplastics and some metals. Its unique advantages, including speed, precision, and cleanliness, have made it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.
In this article, we’ll explore the diverse applications of ultrasonic welding across different sectors and understand why it has become such a crucial technology.
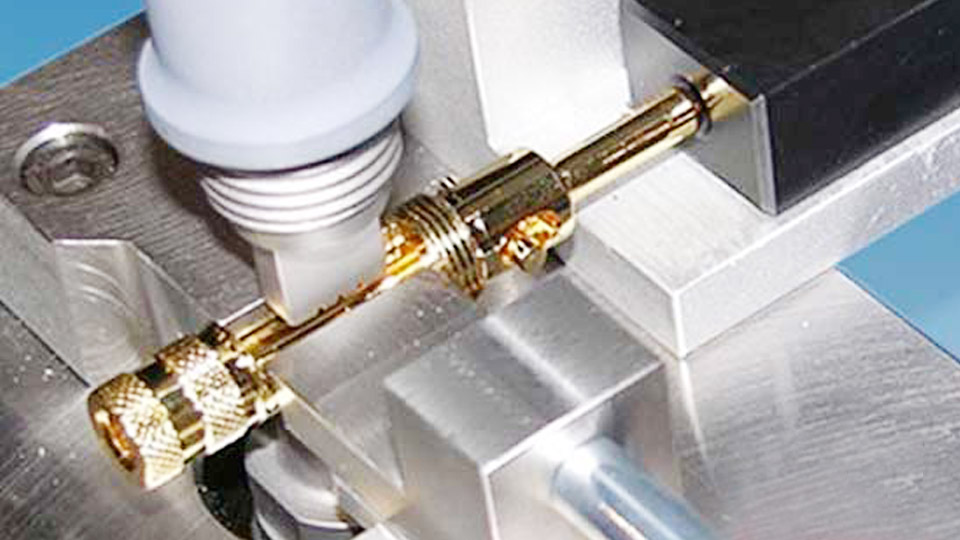

Image by assemblymag
About Ultrasonic Welding
Before delving into its applications, it’s essential to understand what ultrasonic welding is and how it works.
The Process
Ultrasonic welding is an indirect heat welding process that uses ultrasonic waves to join materials. The machine converts high-frequency electrical signals (typically 20-40 kHz) into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations are then amplified and delivered to the materials being joined, generating heat through friction and creating a strong bond.
Key Advantages
Ultrasonic welding offers several benefits that make it attractive for various applications:
- Speed: The process is incredibly fast, often taking just a few seconds.
- Safety: It uses indirect heat, reducing operational hazards.
- Reliability: The machines are dependable with minimal breakdowns.
- Versatility: It can join dissimilar materials, especially useful for plastics.
- Cost-effectiveness: No additional materials like adhesives or solder are required.
- Joint quality: The resulting welds are clean, strong, and often invisible.
Let’s explore how these advantages translate into practical applications across different industries.
Applications in the Medical Industry
The medical industry has embraced ultrasonic welding for its ability to create clean, precise, and contamination-free joints.
Medical Devices and Equipment
Ultrasonic welding is used to manufacture a wide range of medical devices and equipment, including:
- Face masks
- Blood and gas filters
- Arterial filters
- Anesthesia filters
- Pipettes
The technique is particularly valuable for these products due to its ability to create high-quality welded joints without introducing contaminants or causing material degradation.
Sterile Textiles
Many plastic-based textiles used in medical settings are assembled using ultrasonic welding. Examples include:
- Sterile garments
- Hospital gowns
- Surgical drapes
Laboratory and Analytical Equipment
Ultrasonic welding is also employed in the production of various laboratory and analytical equipment, including:
- Membranes
- Filters
- Adapters
- Connectors
The technique’s ability to meet stringent medical requirements in terms of strength, tightness, and near particle-free production makes it ideal for these applications.
Applications in the Automotive Industry
The automotive sector has found numerous uses for ultrasonic welding, particularly in the assembly of plastic components and electrical parts.
Interior Components
Ultrasonic welding is commonly used to assemble various interior components of vehicles, including:
- Door panels
- Instrument panels
- Steering wheels
The process is suitable for these applications due to its use of indirect heat, which doesn’t affect the workpiece, as well as its low capital costs, automation capabilities, and flexibility.
Electrical Components
Many electrical components in vehicles are assembled using ultrasonic welding, including:
- Engine components
- Wiring harnesses (particularly for laying copper wires)
Other Automotive Applications
Ultrasonic welding is also used for:
- Riveting in automotive applications
- Sealing various components
The technique’s speed, precision, and ability to join dissimilar materials make it invaluable in the fast-paced, high-volume production environment of the automotive industry.
Applications in the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry utilizes ultrasonic welding primarily for its accuracy, speed, and ability to join thin, lightweight materials.
Metal Joining
In aerospace applications, ultrasonic welding is most often used to join thin, lightweight sheets of metal, particularly aluminum. This is crucial for maintaining the low weight requirements of aircraft components.
Air Ducts
One of the most common applications of ultrasonic welding in the aerospace industry is the manufacture of air ducts.
Other Aerospace Components
The technique’s precision and reliability make it suitable for creating various other aerospace components where weight, strength, and quality are paramount.
Applications in the Electronics Industry
The electronics industry heavily relies on ultrasonic welding for creating delicate connections and assembling small components.
Circuit Connections
Ultrasonic welding is used to join wired connections and create connections in small, delicate circuits where traditional welding techniques might cause damage.
Electronic Components
The technique is commonly used in the assembly of various electronic components, including:
- Microcircuits
- Computer disks
- Capacitors
- Flash drives
- Electric motors
- Storage media
Advantages in Electronics Manufacturing
Ultrasonic welding is particularly valuable in electronics manufacturing because it allows for:
- Creation of small and delicate circuits
- Greater accuracy and efficiency in assembly
- Reliable connections without the risk of heat damage
Applications in the Packaging Industry
The packaging industry, particularly food packaging, has found numerous applications for ultrasonic welding.
Food Packaging
Ultrasonic welding is often used to seal packages containing heat-sensitive foods. Examples include:
- Blister packs
- Candy wrappers
- Frozen food packaging
- Beverage containers
Special Packaging Applications
The technique is also used for packaging materials that are sensitive to heat or reactive, such as:
- Explosives
- Fireworks
- Heat-reactive chemicals
Advantages in Packaging
Ultrasonic welding is preferred in these applications because it:
- Creates a complete barrier
- Minimizes heat exposure to the packaged contents
- Provides clean, strong seals
Applications in the Consumer Products Industry
The consumer products industry utilizes ultrasonic welding for its efficiency and suitability for mass production.
Toys
Many plastic toys are assembled using ultrasonic welding. The technique’s speed and ability to create strong, clean joints make it ideal for toy manufacturing.
Tools
Various consumer tools, particularly those with plastic components, are often assembled using ultrasonic welding.
Other Consumer Products
The technique is used in the production of a wide range of other consumer goods, especially those made from thermoplastics.
Applications in the Textile Industry
The textile industry has found several applications for ultrasonic welding, particularly in the production of synthetic fabrics and specialized clothing.
Synthetic Fabric Joining
Ultrasonic welding is used to join synthetic fabrics without the need for thread or adhesives. This results in strong, waterproof seams.
Specialized Clothing
The technique is used in the production of various specialized clothing items, including:
- Waterproof garments
- Protective wear
- High-performance sportswear
Emerging Applications and Future Prospects
As technology continues to advance, new applications for ultrasonic welding are constantly emerging.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Ultrasonic welding’s efficiency and lack of additional materials make it an attractive option for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Advanced Materials
As new materials are developed, particularly in the fields of composites and advanced polymers, ultrasonic welding is likely to find new applications in joining these materials.
Miniaturization
With the trend towards smaller, more compact devices, ultrasonic welding’s precision and ability to work with small components will likely become even more valuable.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding has proven to be a versatile and invaluable technique across a wide range of industries. From medical devices to automotive components, from electronic circuits to food packaging, its applications are diverse and continually expanding. The technique’s unique advantages – including speed, precision, cleanliness, and ability to join dissimilar materials – have made it an essential tool in modern manufacturing.
As industries continue to evolve, seeking more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality production methods, ultrasonic welding is likely to play an increasingly important role. Its ability to meet the demanding requirements of various sectors while offering cost-effective and environmentally friendly solutions positions it as a key technology for the future of manufacturing.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.