Choosing the right welding power source is crucial for achieving high-quality welds and ensuring efficient operations. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, a farmer, or a professional welder, selecting the appropriate machine can significantly impact your welding performance and productivity.
This guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when picking a welding power source, helping you make an informed decision that meets your specific needs.

Image by carasalesm
Understanding Your Welding Needs
Before diving into the technical aspects of welding machines, it’s essential to assess your welding requirements:
- Welding Processes: Determine which welding processes you’ll be using most frequently (e.g., Stick, MIG, TIG, Flux-Cored).
- Material Types and Thicknesses: Consider the types of metals you’ll be welding and their typical thicknesses.
- Work Environment: Will you be welding indoors, outdoors, or both? This affects portability and power source requirements.
- Frequency of Use: Are you an occasional welder or will you be using the machine regularly?
- Budget: Establish a realistic budget for your welding power source.
Types of Welding Power Sources
Transformer-Based Machines
- Traditional technology, heavier but often more durable
- Generally less expensive
- Suitable for basic welding tasks
Inverter-Based Machines
- Modern technology, lighter and more portable
- More energy-efficient
- Often provide better arc control and performance
- Usually more expensive
Engine-Driven Welders
- Ideal for outdoor use where electrical power isn’t available
- Can provide both welding power and auxiliary power for tools
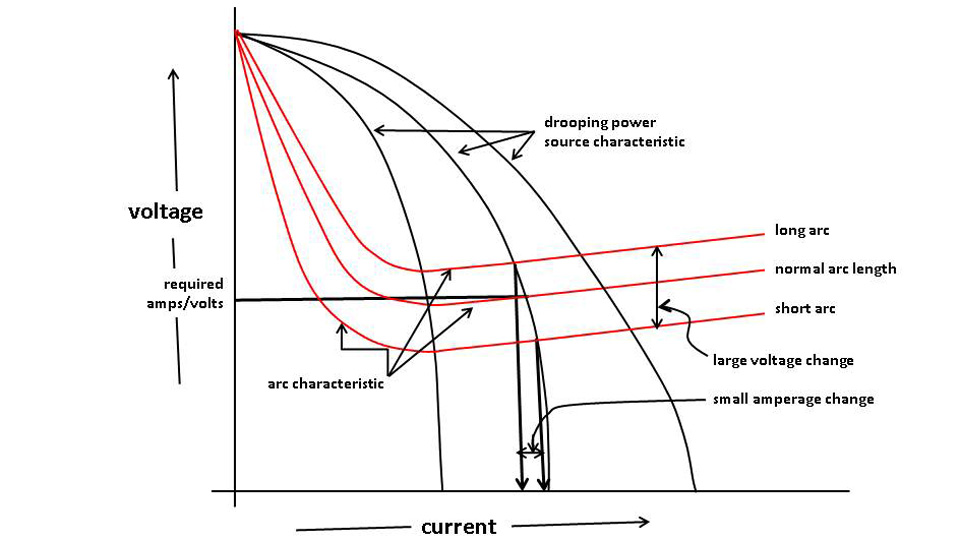
Types of Welding Characteristics by TWI Global
Key Factors to Consider
Power Input Requirements:
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase: Most home and small shop welders use single-phase power (typically 120V or 240V). Three-phase power is more common in industrial settings.
Input Voltage: Ensure the machine can operate on your available power supply. Some machines offer dual voltage capabilities (e.g., 120V/240V).
Output Power and Duty Cycle:
Amperage Range: Choose a machine with an amperage range suitable for your typical welding tasks. For example:
- Up to 1/4″ material: 100-140 amps
- 1/4″ to 3/8″ material: 140-200 amps
- 3/8″ and thicker: 200+ amps
Duty Cycle: This indicates how long the machine can weld continuously in a 10-minute period. Higher duty cycles allow for longer continuous welding times.
Multiprocess Capabilities
- Consider a multiprocess machine if you need flexibility to perform different welding techniques (e.g., Stick, MIG, TIG).
- These machines offer versatility but may compromise on specialized features for individual processes.
Portability
Weight: Inverter-based machines are generally lighter and more portable.
Size: Consider the physical dimensions if you have limited space or need to transport the machine frequently.
Advanced Features
Hot Start: Helps prevent electrode sticking in Stick welding.
Arc Force Control: Improves arc stability and penetration.
Pulse Welding: Offers better control on thin materials and out-of-position welding.
Programmable Memory: Allows saving of preferred settings for quick recall.
Brand Reputation and Support
- Choose reputable brands known for reliability and good customer support.
- Consider the availability of spare parts and service centers in your area.
Accessories and Consumables
- Check the compatibility and availability of accessories like welding guns, electrode holders, and consumables.
Safety Features
- Look for machines with built-in safety features like thermal overload protection and fan-on-demand cooling.
Specific Recommendations for Different User Types
DIY/Hobbyist Welders
- Focus on user-friendly machines with basic features.
- Consider inverter-based machines for their portability and efficiency.
- Look for dual-voltage capabilities (120V/240V) for flexibility.
- A multiprocess machine (e.g., MIG/Flux-Cored/Stick) can be a good all-around choice.
Farmers/Ranchers
- Prioritize durability and portability for field repairs.
- Consider engine-driven welders for remote locations without power access.
- Look for machines with higher amperage outputs (200+ amps) for thicker materials.
- Multiprocess capabilities are beneficial for versatility.
Professional Welders
- Invest in high-quality, industrial-grade machines with advanced features.
- Consider specialized machines for specific welding processes if you focus on particular types of work.
- Look for machines with high duty cycles for continuous operation.
- Pay attention to power efficiency and arc performance for productivity.
Making the Final Decision
Research and Compare
- Read product specifications carefully.
- Compare features and prices across different brands and models.
- Read user reviews and professional evaluations.
Try Before You Buy
- If possible, test the machine or attend demonstrations.
- Some suppliers offer rental options, which can be a good way to test a machine before purchasing.
Consider Future Needs
- While it’s important to meet your current requirements, also think about potential future projects or skill development.
- Investing in a slightly more capable machine might save you from needing to upgrade soon.
Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
- Consider not just the initial purchase price, but also:
- Energy efficiency and operating costs
- Cost of consumables and accessories
- Potential maintenance and repair costs
Warranty and After-Sales Support
- Check the warranty terms and duration.
- Evaluate the manufacturer’s customer support and service network.
Conclusion
Choosing the right welding power source is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your welding projects and overall satisfaction. By carefully considering your specific needs, understanding the key features of different machines, and evaluating the various options available, you can select a welding power source that will serve you well for years to come.
Remember that the best welding machine for you is one that not only meets your current needs but also allows room for growth in your welding skills and projects. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast working on home projects, a farmer maintaining equipment, or a professional welder tackling diverse jobs, there’s a welding power source out there that’s right for you.
Take your time in making this decision, do thorough research, and don’t hesitate to seek advice from experienced welders or welding supply professionals. With the right welding power source, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle your welding tasks efficiently, safely, and with high-quality results.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.