Are you a welding enthusiast looking to dive into the world of stick welding? One of the key factors to consider is the polarity of your welding machine. Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), can be done with either Direct Current (DC) positive or negative polarity. But what’s the difference?
Before we delve into the world of stick welding polarity, let’s take a moment to understand what Direct Current (DC) is. In stick welding, the welding machine produces electrical current that flows through the electrode, creating an arc that melts the metal and forms the weld.
Direct Current can flow in two directions: positive and negative. In DC positive welding, the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the welding machine, while in DC negative welding, the electrode is connected to the negative terminal. The choice of polarity has a significant impact on the welding process and the resulting weld quality.
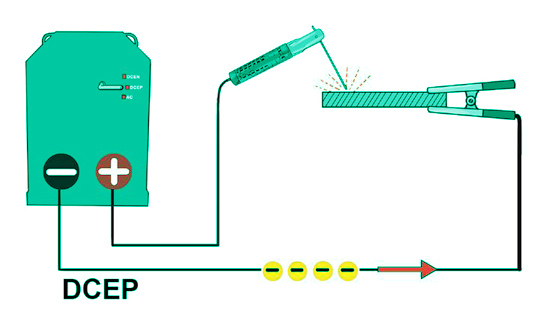
Image by pinterest
Difference between DC Positive and DC Negative in Stick Welding
The main difference between DC positive and DC negative in stick welding lies in the direction of the current flow. In DC positive welding, the current flows from the electrode to the workpiece, creating a strong and deep weld penetration. On the other hand, in DC negative welding, the current flows from the workpiece to the electrode, resulting in a shallow weld penetration.
Apart from the direction of current flow, another key difference lies in the electrode performance. In DC positive welding, the electrode tends to burn faster, resulting in a more stable arc and better control over the weld pool. In DC negative welding, the electrode burns slower, leading to a less stable arc and potentially more spatter.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Positive Stick Welding
DC positive stick welding offers several advantages. Firstly, it provides excellent weld penetration, making it suitable for welding thick materials. The deep penetration ensures strong and durable welds, making it ideal for structural applications. DC positive welding allows for better control over the weld pool, resulting in cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing welds.
DC positive stick welding has its drawbacks as well. The faster electrode burn rate can lead to increased consumption and higher costs. The high heat generated during the process can cause distortion or warping of thin materials. It is important to consider these factors when deciding whether to use DC positive stick welding for your projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Negative Stick Welding
DC negative stick welding also has its own set of advantages. One of the main benefits is the reduced electrode consumption, leading to cost savings in the long run. The slower burn rate of the electrode in DC negative welding allows for longer welding times without the need for frequent electrode changes.
DC negative stick welding has limitations as well. The shallow weld penetration may not be suitable for thicker materials or applications that require strong welds. Additionally, the less stable arc can make it challenging to maintain control over the weld pool, resulting in a less precise and aesthetically pleasing weld.
Applications of DC Positive Stick Welding
DC positive stick welding finds its application in various industries. Its deep weld penetration makes it ideal for welding heavy structural steel, such as beams, columns, and bridge components. It is also commonly used for welding thick materials in construction, shipbuilding, and pipeline industries.
DC positive stick welding is often preferred for welding in tight spaces or overhead positions, as the stable arc and better control allow for easier maneuverability. It is important to consider these applications when deciding whether DC positive stick welding is the right choice for your projects.
Applications of DC Negative Stick Welding
DC negative stick welding also has its own range of applications. The reduced electrode consumption makes it a cost-effective option for long-duration welding projects. This makes it suitable for applications such as pipeline construction, where long welds are required.
DC negative stick welding is commonly used for welding thin materials, such as sheet metal or automotive body panels. The less aggressive weld penetration helps prevent burn-through and distortion of the material, resulting in clean and precise welds.
Choosing the Right Polarity for Your Stick Welding Projects
When it comes to choosing the right polarity for your stick welding projects, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on various factors, including the material thickness, desired weld penetration, and the specific application.
For thick materials or applications that require strong welds, DC positive stick welding is the preferred choice. On the other hand, if you’re working with thin materials or need to minimize distortion, DC negative stick welding may be the better option. It is important to consider these factors and experiment with both polarities to determine which one suits your specific welding needs.
Tips for Successful Stick Welding with DC Positive or DC Negative
Regardless of whether you choose DC positive or DC negative stick welding, there are a few tips that can help you achieve successful welds. Here are some key pointers to keep in mind:
- Clean and prepare the workpiece thoroughly before welding to ensure good electrical contact and minimize contaminants.
- Use the appropriate electrode for the desired polarity and application. Different electrodes have different characteristics and are designed for specific welding purposes.
- Maintain a consistent arc length and travel speed to achieve consistent and uniform welds.
- Practice proper electrode manipulation techniques, such as maintaining a slight drag angle or using a weaving motion, to control the weld pool and prevent defects.
- Monitor the welding parameters, such as current and voltage, to ensure they are within the recommended range for the specific electrode and material being welded.
By following these tips, you can enhance your stick welding skills and achieve high-quality welds, regardless of the polarity you choose.
Conclusion
The choice between stick welding DC positive or negative depends on various factors, including the desired weld penetration, material thickness, and specific application. Both polarities have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to consider these factors before making a decision.
DC positive stick welding offers deep weld penetration and better control over the weld pool, making it ideal for thick materials and structural applications. On the other hand, DC negative stick welding reduces electrode consumption and is suitable for thin materials or applications that require minimal distortion.
The key to successful stick welding lies in understanding the characteristics and applications of both polarities, and experimenting with different techniques to find the best approach for your specific welding needs.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.



