Tig welding can pose health risks due to UV radiation exposure and toxic fumes released. However, with proper safety measures, these risks can be minimized.
Tig welding involves using a high-temperature arc to join metal pieces together. This process produces intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can harm the skin and eyes if proper protection is not worn. The welding process generates fumes and gases that can be harmful if inhaled.

Photo by performanceracing
It is important for welders to use protective gear such as welding helmets, gloves, and ventilation systems to safeguard their health while tig welding. In this blog post, we will explore the potential health hazards of tig welding and provide tips on how to mitigate these risks effectively.
Basics Of Tig Welding
TIG welding emits fumes and gases that can be harmful to your health if inhaled. These include ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and metal fumes. It’s important to use proper ventilation and wear a respirator to protect yourself from the potential health risks associated with TIG welding.
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular welding method that offers precise control and high-quality welds. It utilizes a tungsten electrode to create the weld and a shielding gas to protect the weld area from contamination. Understanding the basics of TIG welding is essential for anyone looking to delve into this welding technique.
Tig Welding Process
The TIG welding process involves several key steps that ensure a successful weld. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Preparation: Before starting the welding process, it’s crucial to properly prepare the workpiece. This includes cleaning the metal surface and removing any contaminants that could affect the quality of the weld.
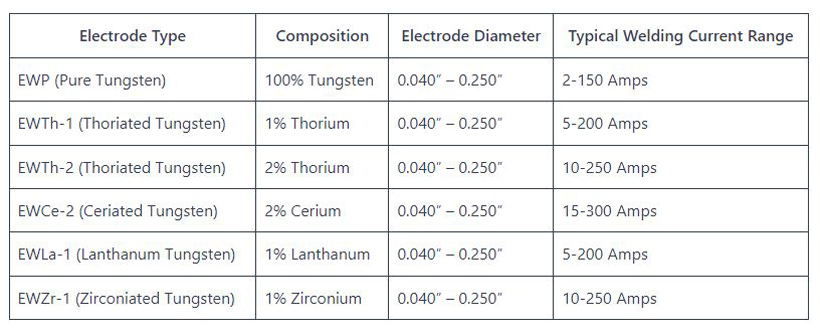
- Electrode Selection: Choosing the right electrode is vital in TIG welding. Tungsten electrodes are commonly used due to their high melting point and excellent conductivity.
- Shielding Gas: TIG welding requires a shielding gas, such as argon or helium, to protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. The choice of gas depends on the specific application and materials being welded.
- Power Supply: A power supply source is needed to generate the electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The power supply controls the welding current and voltage.
- Welding Technique: TIG welding requires a steady hand and precise control. The welder must maintain a consistent arc length and move the torch along the joint at a steady speed to create a uniform weld bead.
- Post-Welding Inspection: After completing the weld, it’s essential to inspect the finished joint for any defects or imperfections. This ensures the weld meets the required quality standards.
Key Components In Tig Welding
Several components play a crucial role in the TIG welding process. Understanding these components is essential for successful TIG welding:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Tungsten Electrode | The tungsten electrode is a non-consumable electrode that carries the welding current and creates the electric arc. |
| Shielding Gas | Shielding gas protects the weld area from atmospheric contamination and ensures a clean, strong weld. |
| Power Supply | The power supply provides the necessary electrical current and voltage for the welding process. |
| Torch | The torch holds the tungsten electrode and directs the flow of shielding gas to the weld area. |
| Filler Metal | In some cases, a filler metal is used to reinforce the weld and provide additional strength. |
By understanding the TIG welding process and the key components involved, you can gain a better grasp of this welding technique. TIG welding offers precise control and high-quality welds, making it a popular choice for various applications.
Potential Health Risks Of Tig Welding
TIG welding involves the use of high-frequency electricity and creates fumes that can be harmful to the welder’s health. The fumes produced by the welding process can cause lung irritation, respiratory problems, and even cancer. It is important for welders to take necessary precautions and wear protective gear to minimize the potential health risks associated with TIG welding.
Exposure To Harmful Gases
One of the potential health risks associated with TIG welding is exposure to harmful gases. During the welding process, various gases are produced, which can pose serious health hazards if inhaled. Welding fumes contain toxic substances such as metal oxides, ozone, and nitrogen oxides, which can lead to respiratory issues, lung damage, and even long-term health complications.
Exposure to these harmful gases can cause symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. Prolonged exposure to welding fumes without proper ventilation or personal protective equipment (PPE) can increase the risk of developing more severe respiratory conditions, including asthma, bronchitis, and even lung cancer.
Ultraviolet And Infrared Radiation
Another health risk associated with TIG welding is the exposure to ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. TIG welding produces intense arcs of light, including UV and IR rays, which can be harmful to the human body. UV radiation can cause skin burns, sunburn-like symptoms, and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. IR radiation, on the other hand, can penetrate deep into the skin, leading to thermal burns and tissue damage.
To protect against UV and IR radiation, welders must wear appropriate protective gear, such as welding helmets with UV and IR filters, long-sleeved clothing, and gloves. Additionally, creating a safe working environment with proper shielding and barriers can help minimize the risk of radiation exposure for both welders and those nearby.
Physical Hazards And Injuries
TIG welding also presents physical hazards and the potential for injuries. The process involves working with high temperatures, electrical currents, and molten metal, which can lead to various accidents if proper safety precautions are not followed.
Common physical hazards associated with TIG welding include electric shock, burns, eye injuries from flying debris, and cuts from sharp edges or hot metal. Welders are at risk of electrical shock if they come into contact with live electrical components or if the welding equipment is faulty. Burns can occur from direct contact with hot metal or sparks, while eye injuries can result from not wearing appropriate eye protection.
To mitigate these risks, welders should always wear protective clothing, including flame-resistant clothing, safety glasses or welding helmets with protective lenses, gloves, and proper footwear. Regular equipment maintenance and adherence to safe welding practices are essential to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of the welder.
Comparing Tig With Other Welding Techniques
TIG welding is generally considered safe, but it does produce fumes and gases that can be harmful if inhaled. Proper ventilation and protective gear are essential to minimize health risks. Compared to other welding techniques, TIG welding may pose fewer health hazards when safety measures are strictly followed.
Health Implications Of Different Welding Methods
Welding is a crucial process in many industries, but it can pose a significant risk to the health of welders. The welding process involves fusing two or more metals together using high temperatures and intense light. The fumes and gases generated during welding can be hazardous to health if inhaled. It is essential to know the health implications of different welding methods to safeguard the health of welders.
Tig Welding Vs Mig And Stick Welding
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is a popular technique for welding thin sections of stainless steel and non-ferrous metals. TIG welding produces less smoke, fumes, and noise than other welding techniques. It also produces a more precise and cleaner weld than MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and stick welding.
MIG welding is suitable for welding thicker sections of steel and aluminum, while stick welding is ideal for outdoor welding. TIG welding is not bad for your health compared to MIG and stick welding. TIG welding produces fewer fumes and smoke than MIG and stick welding, making it a safer option.
MIG welding produces more fumes and smoke than TIG welding due to the wire feed process. Stick welding produces the most fumes and smoke as the welding rod has a flux coating that vaporizes during the welding process. In conclusion, TIG welding is a safer option compared to other welding techniques when it comes to the health implications. It is essential to take adequate safety measures, such as wearing protective equipment and working in a well-ventilated area, to minimize the health risks associated with welding.
Respiratory Concerns In Welding
Respiratory concerns in welding are a crucial aspect to consider for the health and safety of welders. The inhalation of metal fumes, inadequate ventilation, and lack of proper respiratory protection can pose serious risks to the respiratory system. In this section, we will delve into the specific respiratory concerns associated with Tig welding and explore measures to mitigate these risks.
Inhalation Of Metal Fumes
Inhalation of metal fumes during Tig welding presents a significant health hazard. The process of Tig welding produces fumes and gases, including oxides of various metals such as chromium, nickel, and manganese. These fumes can cause respiratory irritation, coughing, and long-term health effects, such as metal fume fever and pulmonary edema.
Ventilation And Respiratory Protection
Proper ventilation is essential to minimize the concentration of metal fumes in the welding environment. Adequate local exhaust ventilation systems and mechanical ventilation can effectively remove fumes from the breathing zone, reducing the risk of inhalation. Utilizing respiratory protection such as NIOSH-approved respirators with appropriate filters can provide an extra layer of defense against the inhalation of metal fumes.
Skin And Eye Protection Measures
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is a popular welding technique used by professionals and DIYers alike. Although TIG welding is an effective way to join metals, it can be hazardous to your health if proper safety measures are not taken. In this blog post, we will discuss the skin and eye protection measures that you should take when performing TIG welding.
Welding Protective Gear
When performing TIG welding, it is essential to wear protective gear to prevent skin and eye injuries. The following are some of the protective gear that you should wear:
| Protective Gear | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Welding Helmet | To protect your face and eyes from the intense light produced during welding. |
| Welding Gloves | To protect your hands from sparks, heat, and electric shock. |
| Welding Apron | To protect your body and clothing from sparks and hot metal. |
Best Practices For Skin And Eye Safety
In addition to wearing protective gear, there are some best practices that you should follow to ensure skin and eye safety:
- Always work in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhaling toxic fumes.
- Use a welding curtain to protect others from the light produced during welding.
- Ensure that your welding helmet has a shade number appropriate for the welding amperage being used.
- Inspect your welding helmet regularly to make sure that the lens is not scratched or damaged.
- Do not touch the welding rod or metal with bare hands immediately after welding, as they may be extremely hot.
- Use a moisturizer on your skin before and after welding to prevent dryness and cracking.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after welding to remove any toxic substances.
By following these skin and eye protection measures, you can reduce the risk of injury and ensure safe TIG welding practices.
Long-term Health Implications
Long-term exposure to TIG welding can have serious implications for your health. Chronic respiratory conditions and the risk of developing cancer are among the most concerning long-term health effects associated with this type of welding.
Chronic Respiratory Conditions
Prolonged exposure to the fumes and gases produced during TIG welding can lead to the development of chronic respiratory conditions. These conditions may include bronchitis, asthma, and pulmonary fibrosis, which can significantly impact your quality of life.
Cancer Risks Associated With Welding
Welding processes, including TIG welding, can expose workers to carcinogenic substances such as hexavalent chromium and nickel compounds. Prolonged exposure to these substances increases the risk of developing lung cancer, laryngeal cancer, and other respiratory system cancers.
Safety Standards And Regulations
When it comes to TIG welding, it is essential to adhere to safety standards and regulations to protect the health and well-being of welders. OSHA guidelines for welders provide a framework for creating a safe welding environment.
Osha Guidelines For Welders
Welders must follow OSHA guidelines to minimize exposure to hazardous fumes and gases. Proper ventilation systems and respiratory protection are crucial for welder safety.
Ensuring A Safe Welding Environment
Employers should provide training on safety procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE) to all welders. Regular monitoring of air quality is also necessary to detect any potential health hazards.
Improving Welder Health And Safety
Training And Education
Proper training and education are essential for welders to understand the potential health hazards associated with their work and to learn how to mitigate these risks. Comprehensive training programs should cover topics such as the safe operation of welding equipment, proper ventilation practices, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
By ensuring that welders are well-educated about health and safety protocols, the industry can significantly reduce the incidence of welding-related health issues.
Innovations In Welding Safety Equipment
Advancements in welding safety equipment have played a crucial role in enhancing the health and well-being of welders. Innovative technologies such as improved ventilation systems, ergonomic welding torch designs, and advanced PPE have contributed to creating a safer working environment for welders. Employing these cutting-edge safety solutions can effectively minimize exposure to harmful fumes, reduce the risk of ergonomic injuries, and enhance overall workplace safety.
Personal Protective Equipment
TIG welding, like any other welding process, requires the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure the safety and health of the welder. Proper selection, use, maintenance, and care of protective gear are crucial for minimizing the potential health hazards associated with TIG welding.
Selection And Use Of PPE
When it comes to TIG welding, selecting and using the right PPE is paramount. Welders must wear a welding helmet with a proper shade lens to protect their eyes from the intense light and radiation emitted during the welding process. Using flame-resistant clothing and gloves is essential to safeguard the skin from sparks and heat.
- Welding helmet with appropriate shade lens
- Flame-resistant clothing and gloves
Maintenance And Care Of Protective Gear
Proper maintenance and care of PPE are vital to ensure its effectiveness in protecting the welder. Regular inspection of the welding helmet, including the lens and headgear, is necessary to identify any damage or wear. Cleaning and storing PPE properly can extend its lifespan and maintain its protective properties.
Emerging Research On Welding And Health
Emerging research suggests that TIG welding can potentially pose health risks to welders due to exposure to hazardous fumes and particles. Studies have shown that proper ventilation and protective equipment can minimize these risks, but further research is needed to fully understand the impact on welders’ health.
Advancements In Welding Technology For Health
Emerging Research on Welding and Health Tig welding is a common method in metal fabrication, but concerns over its impact on health have been on the rise. Recent studies shed light on the potential health risks associated with this welding technique. Research indicates that exposure to welding fumes can lead to respiratory issues and other health complications. Workers exposed to welding fumes are at higher risk of developing lung diseases. In a recent study, researchers found a correlation between prolonged welding exposure and an increased risk of lung cancer.
This emphasizes the importance of proper safety measures in welding environments. Advancements in welding technology have focused on reducing the health risks associated with welding. Innovative ventilation systems and fume extraction tools are being developed to minimize exposure to harmful fumes. New welding equipment with improved filtration capabilities help in reducing the release of hazardous substances into the air.
These advancements aim to create a safer working environment for welders. Employers play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of their workers by providing proper training on safety protocols and investing in the latest welding technologies.
By staying informed about the latest research and advancements in welding technology, welders can protect their health and well-being while pursuing their craft.
Conclusion
While Tig welding has health risks, proper safety measures can minimize them. Regular monitoring and protective gear are crucial for welders. Awareness and caution can help mitigate potential health hazards associated with Tig welding. Stay informed and prioritize safety when engaging in welding activities.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.