Welding technology has come a long way since its inception, with various techniques and processes developed to meet the diverse needs of industries and craftsmen alike. Among these advancements, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding has emerged as a popular and versatile method.
However, as technology progresses, we’ve seen the evolution of MIG welding into more sophisticated forms, namely Pulsed MIG and Double Pulsed MIG. In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between these three welding techniques, their advantages, and the applications where each shines.

Image by red-d-arc
Traditional MIG Welding
Before diving into the more advanced techniques, it’s essential to understand the basics of traditional MIG welding.
What is MIG Welding?
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process that uses a continuously fed wire electrode and a shielding gas to join metals. The process is widely used in various industries due to its versatility, speed, and relative ease of use.
How MIG Welding Works
In MIG welding, an electric arc is formed between the workpiece and the consumable wire electrode, which is continuously fed through a welding gun. The arc heats the base metal and the end of the electrode, causing them to melt and form a weld pool. The shielding gas protects the molten metal from atmospheric contamination.
Advantages of MIG Welding
- Versatility: Can be used on a wide range of metals and thicknesses
- Speed: Faster than many other welding processes
- Easy to learn: Relatively simple for beginners to pick up
- Clean welds: Produces less slag compared to stick welding
Limitations of MIG Welding
- Spatter: Can produce more spatter than advanced techniques
- Heat control: Less precise heat control compared to TIG welding
- Outdoor use: Not ideal for outdoor welding due to wind affecting shielding gas
Introducing Pulsed MIG Welding
Pulsed MIG welding is an advanced form of MIG welding that offers improved control and performance.
What is Pulsed MIG Welding?
Pulsed MIG welding is a variation of the MIG process that uses a pulsing current to control the transfer of molten metal from the wire to the weld pool. This pulsing action alternates between a high peak current and a low background current.
How Pulsed MIG Welding Works
In pulsed MIG welding, the power source rapidly switches between a high peak current and a lower background current. The peak current is responsible for melting the wire and creating a droplet, while the background current maintains the arc but doesn’t melt additional wire. This pulsing action happens many times per second, creating a more controlled metal transfer.
Advantages of Pulsed MIG Welding
- Reduced heat input: Better for welding thin materials
- Improved control: Easier to weld out of position
- Less spatter: Cleaner welds with less post-weld cleanup
- Better penetration: Achieves good penetration without excessive heat
- Improved appearance: Can produce TIG-like weld aesthetics
Applications of Pulsed MIG Welding
Pulsed MIG welding is particularly useful for:
- Welding thin materials
- Out-of-position welding
- Welding aluminum and stainless steel
- Applications requiring minimal heat input
- Projects where weld appearance is important
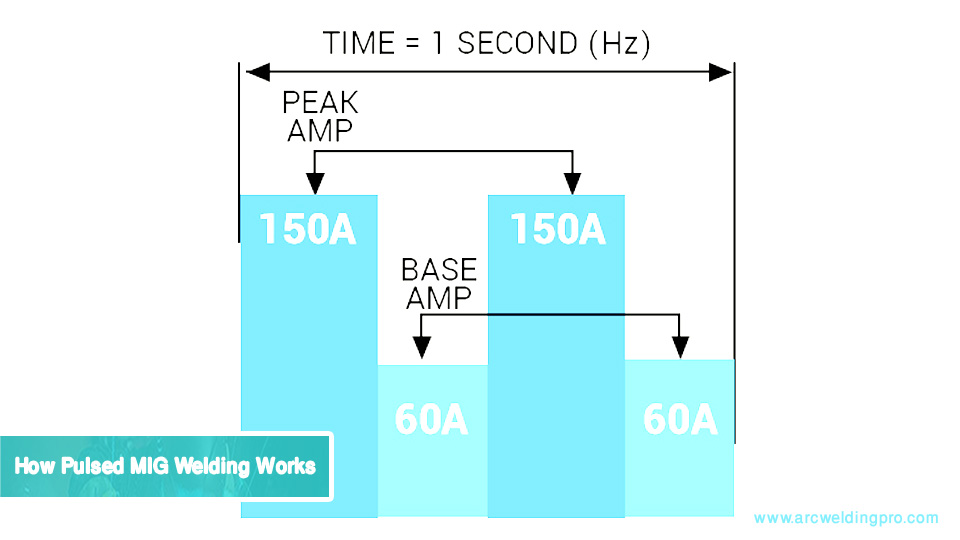
Image by red-d-arc
Exploring Double Pulsed MIG Welding
Double Pulsed MIG welding takes the concept of pulsed welding a step further, offering even more control and precision.
What is Double Pulsed MIG Welding?
Double Pulsed MIG welding, also known as Pulse-on-Pulse welding, is an advanced variation of Pulsed MIG welding. It involves two distinct pulsing actions: the primary pulse (similar to single pulse MIG) and a secondary pulse that modulates the primary pulse.
How Double Pulsed MIG Welding Works
In Double Pulsed MIG welding, the welding machine generates two sets of pulses. The primary pulse controls the metal transfer, similar to single pulse MIG. The secondary pulse modulates the primary pulse, creating alternating periods of high and low heat input. This results in a very precise control of the weld pool and allows for a “stacked dimes” appearance similar to TIG welding.
Advantages of Double Pulsed MIG Welding
- Superior heat control: Even more precise than single pulse MIG
- Excellent for thin materials: Minimizes the risk of burn-through
- TIG-like appearance: Produces welds that closely resemble TIG welding
- Reduced distortion: Minimizes warping in thin materials
- Improved out-of-position welding: Offers excellent control in all positions
Applications of Double Pulsed MIG Welding
Double Pulsed MIG welding excels in:
- Welding very thin materials
- Applications requiring minimal heat input and distortion
- Projects where weld aesthetics are crucial
- Automotive and aerospace industries
- Welding aluminum and other non-ferrous metals

Image by alibaba
Comparing MIG, Pulsed MIG, and Double Pulsed MIG
Now that we’ve explored each technique individually, let’s compare them side by side to understand their differences and when to use each.
Heat Input and Control
- Traditional MIG: Highest heat input, least control
- Pulsed MIG: Reduced heat input, improved control
- Double Pulsed MIG: Lowest heat input, most precise control
Weld Appearance
- Traditional MIG: Standard weld bead appearance
- Pulsed MIG: Improved appearance, can resemble TIG welds
- Double Pulsed MIG: Closest to TIG weld appearance, “stacked dimes” look
Spatter Production
- Traditional MIG: Most likely to produce spatter
- Pulsed MIG: Significantly reduced spatter
- Double Pulsed MIG: Minimal to no spatter
Skill Level Required
- Traditional MIG: Easiest to learn and use
- Pulsed MIG: Requires more skill and understanding
- Double Pulsed MIG: Most complex, requires advanced knowledge
Cost of Equipment
- Traditional MIG: Most affordable
- Pulsed MIG: More expensive than traditional MIG
- Double Pulsed MIG: Most expensive option
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate welding technique depends on various factors. Here are some guidelines to help you choose:
When to Use Traditional MIG
- For general-purpose welding tasks
- When working with thicker materials
- In situations where cost is a primary concern
- For beginners or less experienced welders
When to Opt for Pulsed MIG
- When welding thin materials (but not ultra-thin)
- For out-of-position welding
- When working with aluminum or stainless steel
- In projects requiring reduced heat input and distortion
When to Choose Double Pulsed MIG
- For welding very thin or heat-sensitive materials
- When weld aesthetics are crucial
- In high-precision industries like aerospace or automotive
- For projects requiring the absolute minimum heat input and distortion
Future of MIG Welding Technology
As welding technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in MIG welding techniques. Some potential developments include:
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI-powered welding systems could optimize welding parameters in real-time, adjusting for variations in material thickness, joint geometry, and other factors.
Advanced Synergic Controls
More sophisticated synergic controls could make complex welding techniques like Double Pulsed MIG more accessible to less experienced welders.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Future MIG welding systems may offer even greater energy efficiency, reducing power consumption and operating costs.
Enhanced Monitoring and Quality Control
Advanced sensors and data analysis could provide real-time feedback on weld quality, helping to reduce defects and improve overall productivity.
Conclusion
The evolution from traditional MIG welding to Pulsed MIG and Double Pulsed MIG represents significant advancements in welding technology. Each technique offers unique advantages and is suited to different applications. While traditional MIG remains a versatile and cost-effective option for many projects, Pulsed MIG and Double Pulsed MIG provide superior control, reduced heat input, and improved weld aesthetics for more demanding applications.
As a welder or fabricator, understanding the differences between these techniques and knowing when to apply each one can significantly enhance the quality of your work and expand your capabilities.
Whether you’re working on a simple repair job or a high-precision aerospace component, choosing the right MIG welding technique can make all the difference in achieving the perfect weld.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovations in MIG welding, further expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved with this versatile welding process.
By staying informed about these developments and continually honing your skills, you can ensure that you’re always at the forefront of welding technology, ready to tackle any challenge that comes your way.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.



