Are you interested in learning about Tig welding carbon steel? In this article, we will dive into the details of this welding process and explore its benefits and challenges. Tig welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular technique for joining metals, particularly carbon steel. Its versatility and precision make it an excellent choice for various applications, from automotive repairs to fabrication projects.
When it comes to Tig welding carbon steel, there are a few key factors to consider. The right selection of filler material, the proper heat control, and the right welding technique all play a crucial role in achieving strong and durable welds. We will discuss these factors in detail and provide you with practical tips to improve your Tig welding skills.

Photo by reddit
Whether you are a professional welder looking to enhance your carbon steel welding expertise or a beginner eager to learn the ropes, this article is for you. Get ready to unlock the secrets of Tig welding carbon steel and take your welding skills to the next level.
Advantages of TIG welding carbon steel
Tig welding carbon steel offers several advantages over other welding techniques. One of the biggest advantages is the ability to create high-quality welds with excellent precision. The Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) process provides better control over the heat input, resulting in minimized distortion and improved aesthetics of the weld.
Another advantage of Tig welding carbon steel is its versatility. This welding process can be used for a wide range of carbon steel thicknesses and positions. It allows for welding in various positions, including flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead, making it a versatile technique for different applications.
Tig welding carbon steel produces welds with excellent mechanical properties. The welds are strong, ductile, and have good impact resistance. This makes Tig welding an ideal choice for applications where the welds are subjected to high stress or vibrations.
TIG welding equipment and tools for carbon steel
Before diving into Tig welding carbon steel, it’s important to have the right equipment and tools. Here are the essentials you will need:
TIG welding machine
Invest in a high-quality TIG welding machine that offers precise control over the welding parameters. Look for models that have advanced features like pulse welding and adjustable AC/DC balance for better control over the arc.
Tungsten electrodes
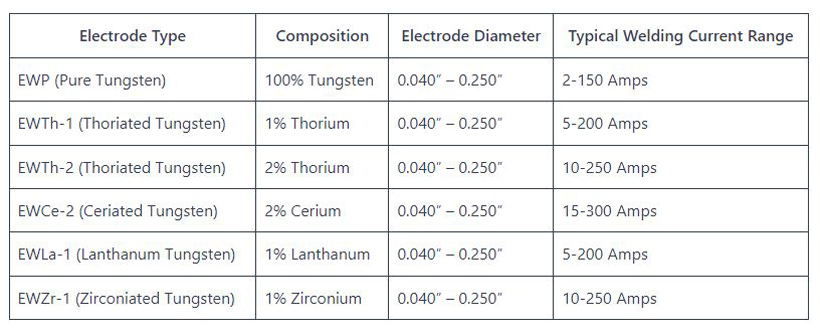
Tungsten electrodes are an integral part of TIG welding. For welding carbon steel, use pure tungsten or thoriated tungsten electrodes. The diameter of the electrode will depend on the thickness of the carbon steel you are working with.
Filler material
Selecting the right filler material is crucial for achieving strong and durable welds. For carbon steel, commonly used filler materials include ER70S-2 and ER70S-6. These filler wires provide good strength and are compatible with carbon steel.
Gas supply
TIG welding requires a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. Argon gas is commonly used for carbon steel welding due to its inert properties. Ensure you have a reliable supply of argon gas and a suitable flow regulator.
With the right equipment and tools in place, you are ready to prepare for Tig welding carbon steel.
Preparation for TIG welding carbon steel
Proper preparation is key to achieving successful welds when Tig welding carbon steel. Follow these steps to ensure your workpiece is ready for welding:
Clean the surface
Before welding, remove any dirt, rust, paint, or other contaminants from the surface of the carbon steel. Use a wire brush or a grinder with a flap disc to clean the surface thoroughly. This will ensure better weld penetration and reduce the risk of defects.
Bevel the edges
If you are welding thick carbon steel plates, consider beveling the edges to create a V-groove joint. This helps in achieving good fusion between the base metal and the filler material. Use a grinder or a milling machine to create the bevel.
Fit-up and alignment
Ensure proper fit-up and alignment of the carbon steel pieces to be welded. The joint should have a small gap (around 1-2mm) to allow for proper penetration and fusion during welding. Use clamps or fixtures to hold the workpieces in place.
By following these preparation steps, you will create a clean and properly aligned workpiece ready for Tig welding.
Proper technique for TIG welding carbon steel
Achieving high-quality welds in carbon steel requires mastering the proper welding technique. Here are some tips to help you improve your Tig welding skills:
Establish the correct arc length
Maintaining the right arc length is crucial for achieving good weld penetration and control. The ideal arc length for Tig welding carbon steel is typically around 1-2mm. Use the foot pedal or torch switch to control the arc length while maintaining a stable arc.
Control the heat input
Carbon steel is prone to overheating, which can result in excessive distortion and weakened welds. Control the heat input by adjusting the welding current and travel speed. A lower heat input is generally recommended for thinner carbon steel, while thicker sections may require higher heat input.
Maintain a consistent travel speed
Consistency is key when it comes to travel speed. Maintain a steady travel speed to ensure even heat distribution and proper fusion between the base metal and the filler material. Avoid excessive weaving or pausing, as it can lead to uneven weld beads or lack of fusion.
Practice these techniques and experiment with different settings to find the optimal parameters for your specific carbon steel welding project.
Common challenges and troubleshooting in TIG welding carbon steel
Tig welding carbon steel can come with its fair share of challenges. Here are some common issues you may encounter and how to troubleshoot them:
Porosity
Porosity refers to the presence of small gas pockets within the weld, resulting in weakened and less durable welds. To reduce porosity, ensure proper gas shielding by maintaining a steady flow of argon gas and checking for any leaks in the gas lines.
Lack of fusion
Lack of fusion occurs when the base metal and filler material do not fully bond together. This can be caused by improper heat control or insufficient travel speed. Adjust the welding parameters to ensure adequate heat input and maintain a consistent travel speed.
Cracking
Cracks can occur in the weld or the heat-affected zone due to excessive heat input or rapid cooling. To prevent cracking, control the heat input and use preheat or post-weld heat treatment if necessary. Additionally, ensure proper joint preparation and fit-up to reduce stress concentrations.
By understanding these common challenges and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting techniques, you can overcome them and achieve high-quality welds in carbon steel.
Safety precautions for TIG welding carbon steel
Safety should always be a top priority when Tig welding carbon steel. Here are some essential safety precautions to follow:
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Wear appropriate PPE, including a welding helmet with a proper shade, welding gloves, flame-resistant clothing, and safety glasses. Protect your skin and eyes from harmful UV radiation and sparks.
Ventilation
Ensure proper ventilation in the welding area to remove fumes and gases generated during the welding process. Welding in a well-ventilated area or using local exhaust ventilation can help protect against respiratory hazards.
Fire safety
Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and be aware of potential fire hazards. Carbon steel welding can produce sparks and hot metal, so clear the area of flammable materials and have fire safety measures in place.
Electrical safety
Inspect the welding equipment and cables regularly for any damages or exposed wires. Use insulated tools and avoid contact with live electrical parts. Follow proper grounding procedures to prevent electric shock.
Following these safety precautions will help create a safe working environment and protect yourself and others during Tig welding carbon steel.
Best practices for TIG welding carbon steel
To achieve the best results when Tig welding carbon steel, consider the following best practices:
Practice, practice, practice
Tig welding requires skill and control, which can only be developed through practice. Take the time to practice on scrap pieces of carbon steel before working on critical projects. This will help you refine your technique and gain confidence.
Maintain proper electrode sharpening
Tungsten electrodes should have a sharp and clean tip for optimal arc stability and control. Use a dedicated tungsten electrode grinder or a bench grinder to sharpen the electrode to a fine point. Replace the electrode when it becomes worn or contaminated.
Monitor weld quality
Inspect the welds regularly to ensure they meet the desired quality standards. Use visual inspection techniques, such as dye penetrant testing or magnetic particle testing, to detect any defects or discontinuities in the welds.
Seek professional guidance
If you encounter difficulties or want to enhance your skills further, consider seeking guidance from experienced welders or attending welding workshops or courses. Learning from experts can provide valuable insights and help you overcome any challenges you may face.
By following these best practices, you can consistently produce high-quality welds and continuously improve your Tig welding skills in carbon steel.
Recommended filler metals for TIG welding carbon steel
Choosing the right filler material is essential for achieving strong and durable welds in carbon steel. Here are some commonly recommended filler metals for Tig welding carbon steel:
ER70S-2
This filler wire is suitable for welding mild and low-alloy carbon steels. It provides good strength and is known for its ease of use and versatility. ER70S-2 can be used for a wide range of carbon steel applications, including structural welding and general fabrication.
ER70S-6
Similar to ER70S-2, ER70S-6 is a popular filler wire for carbon steel welding. It offers higher tensile strength and is particularly suitable for welding high-strength carbon steels. ER70S-6 is commonly used in automotive applications, pressure vessels, and heavy equipment fabrication.
When selecting the filler material, consider the specific requirements of your welding project, including the carbon steel grade, joint design, and desired mechanical properties.
Conclusion
Tig welding carbon steel offers numerous advantages, including excellent precision, versatility, and strong welds. By understanding the key factors and following the proper techniques, you can achieve high-quality welds in carbon steel.
To prioritize safety by wearing appropriate PPE and following safety precautions. Practice regularly to improve your skills, and seek guidance from professionals when needed.
With the right equipment, proper preparation, and best practices, you can master the art of Tig welding carbon steel and take your welding skills to new heights.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.