TIG welding galvanized sheet metal requires proper ventilation to avoid zinc fumes exposure. Use a respirator for safety.
Welding galvanized sheet metal can be challenging due to the zinc coating that can produce harmful fumes when heated. It is crucial to follow safety precautions and utilize the appropriate equipment to ensure a successful weld. We will explore the process of TIG welding galvanized sheet metal, including the necessary steps, safety measures, and best practices to achieve optimal results.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced welder, understanding the techniques involved in welding galvanized sheet metal can help you produce high-quality and durable welds. Let’s dive in and learn more about this specialized welding process.

Image by weldinganswers
About Tig Welding Galvanized Metal
When it comes to welding galvanized sheet metal, TIG welding is a popular method known for its precision and versatility. In this section, we will delve into the basics of TIG welding galvanized metal and explore the characteristics of galvanized sheet metal that make it unique from other materials.
Basics Of Tig Welding
TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is a precise welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the weld. This method is ideal for welding thin materials such as galvanized sheet metal due to its low heat input and precise control. The welding area is protected from atmospheric contamination by an inert gas, typically argon, which contributes to producing high-quality welds.
Galvanized Metal Characteristics
Galvanized sheet metal is coated with a layer of zinc to protect the underlying steel from corrosion. When welding galvanized metal, it’s important to note that the zinc coating vaporizes at the welding temperature, releasing harmful fumes. Proper ventilation and respiratory protection are essential when working with galvanized sheet metal to prevent exposure to these fumes. The presence of zinc can affect the weld quality, requiring specific techniques and considerations during the TIG welding process.
Safety First: Precautions And Gear
Tig welding galvanized sheet metal can be a highly effective method for joining metals, but it is essential to prioritize safety when working with this material. By taking the necessary precautions and using the right protective gear, you can ensure a safe and productive welding experience.
Protective Equipment
Before starting any welding project involving galvanized sheet metal, it is crucial to equip yourself with the necessary protective gear. This gear will not only protect you from potential hazards but also ensure that you can focus on your work without any distractions or concerns.
The following table outlines the essential protective equipment you should have:
| Protective Equipment | Description |
|---|---|
| Welding Helmet | A helmet with a darkened lens to shield your eyes from the intense light and harmful UV radiation produced during welding. |
| Welding Gloves | Heat-resistant gloves that provide protection against sparks, hot metal, and potential burns. |
| Welding Jacket | A flame-resistant jacket that covers your upper body and arms, shielding you from sparks, heat, and potential molten metal splatter. |
| Respiratory Protection | A respirator or mask specifically designed for welding, capable of filtering out harmful fumes and particulate matter. |
| Ear Protection | Earplugs or earmuffs to protect your hearing from the loud noise produced during welding. |
| Steel-Toed Boots | Sturdy boots with steel reinforcement to protect your feet from falling objects and potential hazards on the work site. |
Ventilation Requirements
Proper ventilation is crucial when welding galvanized sheet metal as it releases zinc fumes, which can be hazardous when inhaled. Ensuring adequate airflow in your workspace will help minimize your exposure to these fumes and create a safer environment.
Here are some ventilation recommendations to follow:
- Work in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors. If working indoors, ensure that there is proper ventilation, such as exhaust fans or open windows and doors.
- Position your workbench or welding area near the source of ventilation to effectively remove fumes from the vicinity.
- Consider using a fume extractor or ventilation system designed specifically for welding to effectively capture and remove hazardous fumes.
- Wear a respirator or mask with appropriate filters to further protect yourself from inhaling harmful fumes.
By adhering to these ventilation requirements, you can minimize your exposure to zinc fumes and maintain a healthier work environment.
Preparation Steps For Welding
To prepare for TIG welding galvanized sheet metal, start by cleaning the metal surface thoroughly to remove any zinc residue. Next, ensure proper ventilation in the work area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Use a dedicated stainless steel wire brush to remove the galvanized coating before welding.
Before welding galvanized sheet metal, it is essential to prepare the metal surface for the welding process. Here are the preparation steps that you should follow:
Cleaning And Degreasing
The first step in preparing galvanized sheet metal for welding is cleaning and degreasing. You can use a wire brush or grinder to remove any rust, dirt, or other contaminants from the surface of the metal. Then, use a degreaser to clean the metal surface thoroughly. It is crucial to ensure that the metal is entirely free of any contaminants before proceeding to the next step.
Removing Zinc Coating
The next step in preparing galvanized sheet metal for welding is to remove the zinc coating. The zinc coating on the metal surface can create toxic fumes when heated during the welding process. You can remove the zinc coating by grinding it off or using a chemical solution. Ensure that you remove the coating from both sides of the metal and the edges.
Applying Welding Flux
After removing the zinc coating, the next step is to apply welding flux to the metal surface. Welding flux helps to protect the metal from the air and prevents oxidation during the welding process. You can apply welding flux using a brush or by dipping the metal into the flux. Ensure that you apply the welding flux to both sides of the metal and the edges.
Clamping The Metal
To prevent warping or distortion during the welding process, it is essential to clamp the metal into place. Ensure that the metal is securely clamped to the work surface and that it does not move during the welding process.
Setting Up The Welding Machine
The final step in preparing galvanized sheet metal for welding is to set up the welding machine. Ensure that you use the appropriate settings for the metal thickness and the welding process. It is also crucial to use the appropriate welding electrode for the metal type.
Preparing galvanized sheet metal for welding is critical to ensure a successful welding process. By following these preparation steps, you can ensure that the metal surface is clean, free of contaminants, and ready for welding.
Setting Up Your Tig Welder
Setting up your TIG welder correctly is crucial when working with galvanized sheet metal. By ensuring that your welder is properly configured, you can achieve high-quality welds and maintain a safe working environment.
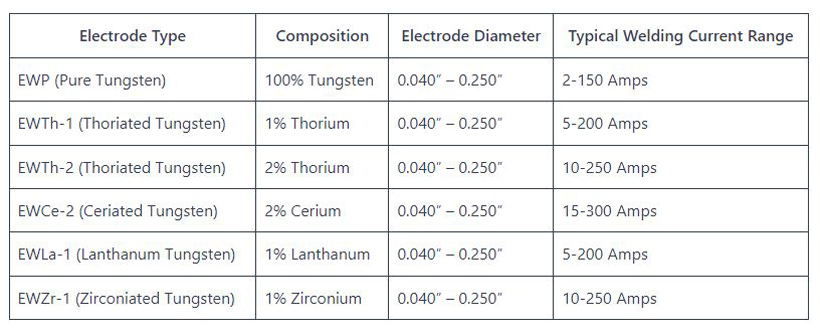
Choosing The Right Electrode
When TIG welding galvanized sheet metal, selecting the appropriate electrode is essential for achieving optimal results. Use a zirconiated tungsten electrode as it offers excellent performance when working with galvanized materials. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist contamination makes it ideal for this application.
Adjusting The Welder Settings
Properly adjusting your TIG welder settings is vital for welding galvanized sheet metal effectively. Ensure that the polarity is set to DCEN (Direct Current Electrode Negative) to prevent excessive spatter and maintain better control over the welding process. Adjust the amperage and gas flow rate to suit the thickness of the galvanized sheet metal being welded, ensuring a smooth and precise welding operation.
Welding Techniques For Galvanized Metal
Seam Welding Tips
Use a low heat setting to prevent zinc evaporation.
Ensure proper ventilation to avoid fume inhalation.
Keep a steady hand and maintain a consistent speed.
Avoiding Warping And Distortion
Preheat the metal to reduce internal stresses.
Use clamps to secure the metal in place during welding.
Implement a backstepping technique to minimize heat buildup.
Post-welding Processes
After TIG welding galvanized sheet metal, post-welding processes are crucial for ensuring the durability and longevity of the weld. These processes include cleaning the weld area to remove any zinc residue, applying a zinc-rich primer to protect against corrosion, and heat treating to relieve any residual stresses in the metal.
Cooling And Cleaning
After completing the Tig welding process on galvanized sheet metal, it is crucial to carry out proper post-welding processes to ensure the integrity and longevity of the weld. One of the essential steps in this process is cooling and cleaning.
Once the weld is completed, the welded area needs to cool down gradually to prevent any potential distortion or damage. Rapid cooling can lead to the formation of stress cracks, compromising the strength of the weld.
To achieve a controlled cooling process, it is recommended to allow the weld to air cool naturally. Avoid using any external cooling methods such as water or compressed air, as they may result in thermal shocks that can weaken the weld.
Once the weld has cooled down, it is essential to clean the surface to remove any contaminants, such as oxides, slag, or spatter. These impurities can negatively affect the appearance and quality of the weld, making it susceptible to corrosion or other defects. Use a wire brush or a suitable cleaning tool to remove the debris, ensuring a clean and smooth surface for further post-welding processes.
Inspecting The Weld
Inspecting the weld is a crucial step in the post-welding processes to ensure the weld’s quality and adherence to specifications. It is necessary to visually examine the weld for any visible defects or inconsistencies. Here are some key points to consider during the inspection:
- Check for any signs of porosity, which appear as small cavities or holes in the weld. These voids can weaken the weld and compromise its strength.
- Look for any cracks or discontinuities that may have formed during the welding process. Cracks can lead to weld failure and should be addressed promptly.
- Ensure that the weld has proper penetration and fusion. Incomplete penetration or lack of fusion can result in weak joints that are prone to failure under stress.
- Inspect the weld for any undercutting, which is a groove formed along the weld’s edges. Undercutting can reduce the overall strength of the weld.
- Check for any excessive spatter or splatter, as it can affect the weld’s appearance and lead to potential defects.
By thoroughly inspecting the weld, any necessary repairs or adjustments can be made to ensure its quality and adherence to the required standards.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
When troubleshooting common problems with Tig welding galvanized sheet metal, it is important to ensure proper ventilation to prevent the release of toxic fumes. Using the correct welding techniques and cleaning the galvanized surface thoroughly can help achieve better welding results.
Tig welding galvanized sheet metal can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to troubleshooting common problems. However, with the right techniques and knowledge, you can overcome these challenges and produce high-quality welds. In this section, we will cover two common problems that you may encounter when tig welding galvanized sheet metal – porosity and spatter.
Dealing With Porosity
Porosity is a common problem that occurs when small pockets of gas get trapped in the weld. This can weaken the weld and make it more prone to cracking. To deal with porosity, follow these tips:
- Make sure the surface of the metal is clean and free from any contaminants before welding. This includes any oil, grease, or rust.
- Adjust your welding technique to reduce the amount of heat input. This will help to minimize the amount of gas that gets trapped in the weld.
- Use a shielding gas with a higher percentage of Argon. This will help to displace any gas that may be trapped in the weld.
Controlling Spatter
Spatter occurs when small droplets of molten metal are expelled from the weld and adhere to the surrounding metal. This can be unsightly and may even cause damage to the surrounding metal. To control spatter, follow these tips:
- Use a lower amperage setting to reduce the amount of heat input. This will help to minimize the amount of molten metal that is expelled from the weld.
- Ensure that the welding torch is held at the correct angle and distance from the metal. This will help to minimize the amount of spatter that is generated.
- Use a welding wire with a lower diameter. This will help to reduce the amount of molten metal that is generated during the welding process.
By following these tips, you can effectively troubleshoot common problems that may occur when tig welding galvanized sheet metal. Remember to always prioritize safety and take the necessary precautions when welding.
Advanced Tips For Professional Results
When it comes to welding galvanized sheet metal, employing advanced techniques is essential for achieving professional results. From pulse welding to achieving smooth finishes, mastering these methods is key to producing high-quality welds on galvanized surfaces.
Pulse Welding Techniques
Pulse welding offers several advantages when working with galvanized sheet metal. By pulsing the amperage, you can effectively control heat input, minimizing the risk of zinc vaporization and reducing the likelihood of spatter. This technique also allows for better control of the weld pool and can result in a cleaner, more precise weld.
Achieving Smooth Finishes
Achieving smooth finishes on galvanized sheet metal requires attention to detail and finesse. To minimize spatter and create clean, uniform welds, ensure that the material is free from contaminants and that the welding parameters are carefully dialed in.
Using the proper filler material and maintaining consistent travel speed can contribute to the creation of smooth, visually appealing welds.
Conclusion
Tig welding galvanized sheet metal requires proper ventilation and safety precautions. The process involves removing zinc coating to avoid harmful fumes. By following best practices, you can achieve strong, clean welds on galvanized sheet metal. Mastering this technique opens up diverse fabrication opportunities.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.