Welcome to the world of TIG welding! Whether you are a beginner or an experienced welder, this article is packed with valuable tips and tricks to help you master the art of TIG welding. From choosing the right equipment and setting up your workstation to perfecting your welding technique, we’ve got you covered. Discover how to achieve clean and precise welds, troubleshoot common issues, and unlock the secrets of TIG welding success.

Photo by ambicasteels
So, grab your helmet and get ready to dive into this comprehensive guide that will take your TIG welding skills to the next level. Let’s ignite the spark and create flawless welds together!
About TIG welding
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a welding technique known for its precision and clean welds. Unlike other welding methods, TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the weld. This allows for greater control and accuracy, making it ideal for intricate and high-quality welds.
To understand TIG welding, it’s important to grasp the basics of its process. The electrode, typically made of tungsten, is connected to the welding machine’s negative terminal. The workpiece, on the other hand, is connected to the positive terminal. As the electrode emits an arc, the tungsten tip becomes hot and creates a weld pool. The weld pool is then fused with the workpiece, resulting in a strong and precise weld.
Advantages of TIG welding
TIG welding offers several advantages over other welding methods. One of the major benefits is the ability to weld a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and more. This versatility makes TIG welding suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive repairs to aerospace components.
Another advantage of TIG welding is the ability to produce clean and visually appealing welds. The precise control over heat input and the absence of spatter ensure minimal post-weld cleaning, saving you time and effort. TIG welding allows for welds with superior mechanical properties, such as high strength and corrosion resistance.
TIG welding equipment and setup
Before diving into TIG welding, it’s essential to have the right equipment and set up your workspace properly. Here are some key factors to consider:
Welding machine
Invest in a high-quality TIG welding machine that suits your needs. Look for features like adjustable amperage control, pulse welding capability, and AC/DC functionality for welding different materials.
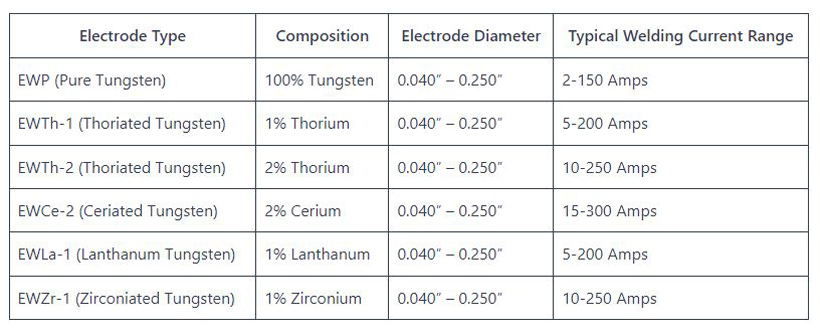
Tungsten electrode selection
Choose the appropriate tungsten electrode based on the material you’re welding. Thoriated tungsten is commonly used for steel alloys, while pure tungsten is suitable for aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Gas selection
Select the right shielding gas based on the material being welded. Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas for TIG welding, providing excellent coverage and preventing contamination of the weld.
Gas flow and pressure
Set the gas flow rate and pressure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Proper gas coverage is crucial for shielding the weld pool and ensuring a clean weld.
Grounding
Ensure proper grounding of the workpiece to maintain a stable arc and prevent electrical interference.
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Always wear appropriate PPE, including a welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing, to protect yourself from the intense heat and harmful UV radiation.
By having the right equipment and a well-organized workspace, you can create a conducive environment for successful TIG welding.
TIG welding techniques for beginners
If you’re new to TIG welding, it’s essential to start with the fundamentals. Here are some techniques to help you get started:
Arc initiation
To start the arc, gently touch the tungsten electrode to the workpiece, lift it slightly, and establish a stable arc. Practice this technique to achieve consistent and controlled arc initiation.
Torch positioning
Hold the TIG torch at a comfortable angle, typically between 10 to 15 degrees from vertical. Maintain a consistent torch-to-work distance of around 1/8 inch to ensure proper heat input and arc stability.
Travel speed
Maintain a steady travel speed to control heat input and prevent overheating. Too slow of a travel speed can lead to excessive heat, while too fast can result in insufficient penetration. Practice maintaining a consistent travel speed for optimal results.
Filler rod manipulation
Add filler rod material to the weld pool using your non-dominant hand. Control the flow of the filler rod to achieve a uniform weld bead and prevent excessive buildup.
Weld bead control
Focus on creating a smooth and consistent weld bead. Avoid excessive weaving or oscillation, as it can lead to uneven heat distribution and an inconsistent weld appearance.
Remember, practice makes perfect. Take the time to master these basic techniques before moving on to more advanced welding applications.
Common TIG welding mistakes to avoid
Even experienced welders can fall into common pitfalls when TIG welding. Here are some mistakes to be aware of and avoid:
Insufficient gas coverage
Inadequate shielding gas coverage can result in weld contamination and porosity. Ensure proper gas flow and coverage to maintain a clean weld environment.
Incorrect tungsten grinding
Improperly ground tungsten electrodes can lead to inconsistent arc starts and unstable arcs. Use a dedicated tungsten grinder or a bench grinder with a dedicated grinding wheel to achieve a precise and consistent electrode tip shape.
Excessive heat input
Applying too much heat can cause distortion, warping, and burn-through. Control the heat input by adjusting the amperage and travel speed to maintain a balanced and controlled weld.
Lack of proper joint preparation
Insufficient joint preparation, such as inadequate cleaning and beveling, can result in poor weld penetration and weak joints. Take the time to properly clean and prepare the joint before welding.
Inconsistent torch angle
Inconsistent torch angle can lead to inconsistent heat distribution and weld appearance. Practice maintaining a consistent torch angle throughout the weld to achieve uniform results.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking the necessary precautions, you can avoid potential welding issues and achieve high-quality welds.
TIG welding tips for improved weld quality
To further enhance your TIG welding skills, consider implementing the following tips:
Choose the right tungsten electrode
Select the appropriate tungsten electrode based on the material being welded. Different materials require different electrode compositions to achieve optimal results.
Focus on cleanliness
Ensure the workpiece and welding area are clean and free from contaminants. Any dirt, grease, or oxide layers can negatively impact weld quality and integrity.
Control heat input
Proper heat control is crucial for achieving consistent and high-quality welds. Avoid overheating the workpiece by adjusting the amperage, travel speed, and torch angle as needed.
Maintain proper weld pool balance
Achieving the right balance between the weld pool and the torch angle is essential for a clean and uniform weld. Practice maintaining a balanced weld pool to achieve optimal results.
Use back purging for critical welds
When welding materials that are prone to oxidation, such as stainless steel, consider using back purging. Back purging involves introducing an inert gas on the backside of the weld to prevent oxidation and ensure a clean and strong weld.
Implementing these tips can significantly improve the quality and aesthetics of your TIG welds, setting you apart as a skilled welder.
TIG welding safety precautions
Safety should always be a top priority when engaging in any welding activity. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
Proper ventilation
Ensure adequate ventilation in your workspace to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes and gases. If working in a confined space, use exhaust fans or ventilation systems to maintain clean air.
Eye protection
Always wear a welding helmet with the appropriate shade lens to protect your eyes from the intense UV radiation produced during TIG welding.
Protective clothing and equipment
Wear flame-resistant clothing, welding gloves, and boots to shield yourself from sparks, molten metal, and potential burns. Long-sleeved shirts and pants made of natural fibers are recommended.
Fire prevention
Keep a fire extinguisher within reach and remove any flammable materials from your work area. Be vigilant about potential fire hazards and take necessary precautions to prevent accidents.
Electrical safety
Ensure the welding machine is properly grounded and that all electrical connections are secure. Avoid touching live electrical parts and be cautious of electrical shock hazards.
Training and certification
Obtain proper training and certification in TIG welding techniques and safety procedures. Continuous education and staying updated on best practices are essential for safe and effective welding.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
Choosing the right TIG welding filler material
Selecting the appropriate filler material is crucial for achieving strong and durable welds. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a TIG welding filler material:
Material compatibility
Ensure the filler material is compatible with the base metal being welded. Different materials require specific filler materials to achieve proper fusion and mechanical properties.
Matching strength properties
Consider the required strength and mechanical properties of the final weld joint. Choose a filler material that matches or exceeds the strength of the base metal for optimal performance.
Corrosion resistance
If welding materials that are prone to corrosion, such as stainless steel, select a filler material with high corrosion resistance to maintain the integrity of the weld joint.
Ease of use
Some filler materials are easier to handle and feed into the weld pool, especially for beginners. Consider the ease of use and feedability when selecting a filler material.
Consult welding reference guides, material specifications, and experienced welders to determine the most suitable filler material for your specific welding application.
Troubleshooting TIG welding issues
Even the most experienced welders encounter welding issues from time to time. Here are some common TIG welding problems and their potential solutions:
Porosity
Porosity refers to the presence of small gas pockets within the weld. It is often caused by inadequate shielding gas coverage or contamination. Ensure proper gas flow, gas coverage, and cleanliness to minimize porosity.
Cracking
Cracking can occur due to excessive heat input, improper joint preparation, or mismatched filler material. Control heat input, properly prepare joints, and use compatible filler materials to prevent cracking.
Tungsten contamination
Tungsten contamination can result in weld defects and inconsistent arc behavior. Avoid touching the tungsten electrode to the workpiece or filler rod to prevent contamination. Proper tungsten grinding and handling techniques are crucial to avoid contamination issues.
Lack of fusion
Insufficient fusion occurs when the weld fails to penetrate the base metal adequately. Ensure proper joint preparation, sufficient heat input, and proper travel speed to achieve proper fusion.
Weld distortion
Excessive heat input or improper welding technique can cause weld distortion. Control heat input, use appropriate tack welds to hold parts in position, and implement proper welding sequences to minimize distortion.
By identifying and troubleshooting these common welding issues, you can overcome challenges and achieve consistent and high-quality welds.
Conclusion
TIG welding is a versatile and precise welding technique that requires skill, practice, and attention to detail. By understanding the fundamentals, implementing best practices, and avoiding common mistakes, you can elevate your TIG welding skills to new heights.
Remember to invest in quality equipment, set up your workspace properly, and prioritize safety at all times. With the right techniques, filler materials, and troubleshooting knowledge, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a master of TIG welding.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.