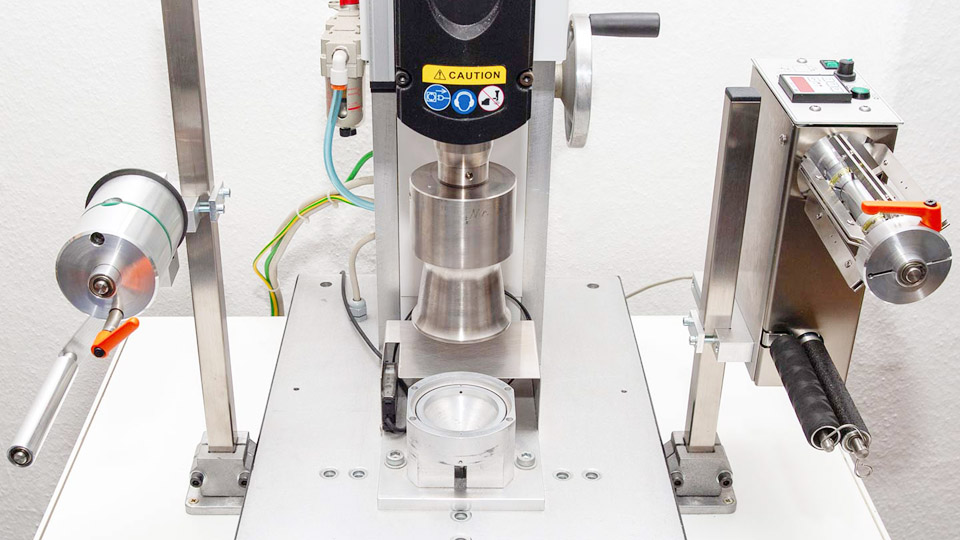
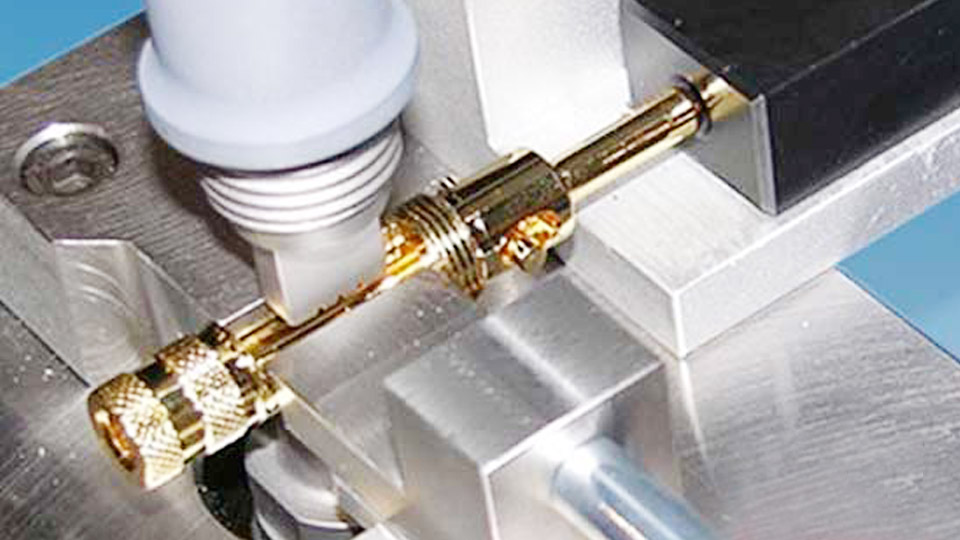
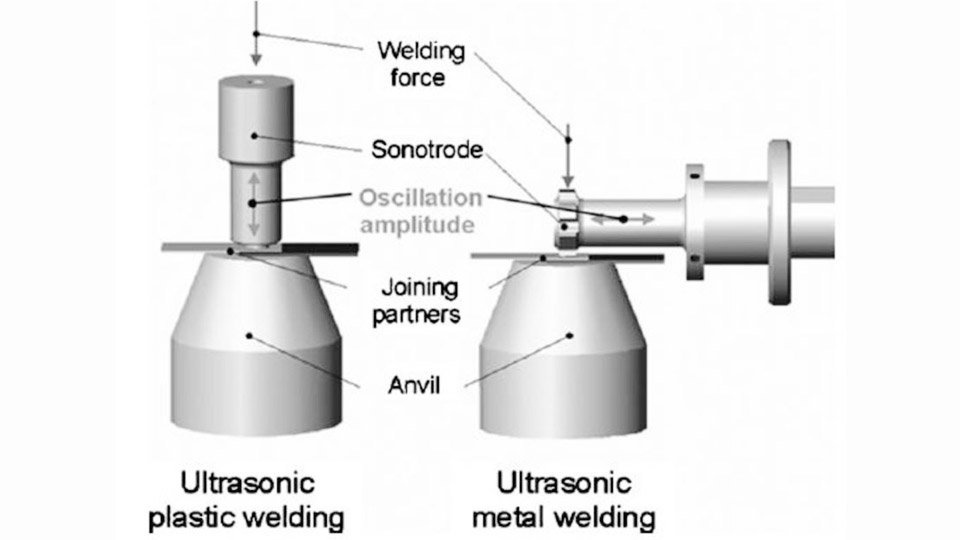
Ultrasonic welding is a versatile and efficient process used to join materials, particularly thermoplastics and metals, through high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations. This process has gained popularity across various industries due to its speed, precision, and ability to create strong bonds without the need for additional materials like adhesives or solder. Understanding what ultrasonic welding is used for can help illustrate its importance and versatility in modern manufacturing.

Image by dizo-global
What is Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding is a solid-state welding technique that uses high-frequency acoustic vibrations to join materials. Unlike traditional welding methods that rely on external heat sources, ultrasonic welding generates heat through friction created by ultrasonic vibrations at the interface of the materials being joined. This process is fast, clean, and capable of producing high-quality, reliable bonds.
Key Features of Ultrasonic Welding
- No Need for Additional Materials: Ultrasonic welding does not require adhesives, solder, or mechanical fasteners, which simplifies the assembly process and reduces costs.
- Environmentally Friendly: The process does not produce fumes, emissions, or waste, making it suitable for applications in cleanroom environments.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Ultrasonic welding can complete a joint in just a few seconds, making it ideal for high-volume production lines.
Automotive Industry Applications
Ultrasonic welding is extensively used in the automotive industry to join various plastic and metal components. The process offers the speed and reliability needed for mass production while maintaining the quality required for automotive parts.
Plastic Components
- Dashboard Assemblies: Ultrasonic welding is used to assemble plastic dashboard components, ensuring a secure and seamless finish.
- Interior Trim: Door panels, center consoles, and other interior trim pieces are often joined using ultrasonic welding to achieve strong, aesthetically pleasing joints.
- Headlamp Assemblies: The plastic lenses and housings of automotive headlamps are joined using ultrasonic welding, providing a watertight seal that protects the internal components.
Electrical and Electronic Components
- Wiring Harnesses: Ultrasonic welding is used to join electrical connections in wiring harnesses, providing reliable and corrosion-resistant joints.
- Sensors and Connectors: Various sensors and connectors, critical to vehicle safety and performance, are assembled using ultrasonic welding to ensure robust connections.
Electronics Industry Applications
The electronics industry relies on ultrasonic welding for assembling delicate components without the risk of heat damage. The precision and control offered by ultrasonic welding make it ideal for electronic assemblies.
Circuit Boards and Microelectronics
- Microcircuit Connections: Ultrasonic welding is used to bond tiny wires and components in microcircuits, where precision and reliability are critical.
- Battery Assemblies: The process is also used in the assembly of battery packs, ensuring strong electrical connections without the need for soldering.
Plastic Enclosures
- Casings for Consumer Electronics: Plastic casings for items like smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics are often assembled using ultrasonic welding, providing a clean and durable finish.
Medical Device Applications
Ultrasonic welding plays a significant role in the medical device industry, where the need for sterile and precise assembly is paramount. The process is well-suited for joining plastic components used in disposable and reusable medical devices.
Disposable Medical Products
- IV Tubes and Catheters: Ultrasonic welding is used to join the plastic components of IV tubes and catheters, ensuring strong, leak-proof connections.
- Filters and Respiratory Masks: The assembly of plastic parts in medical filters and masks is achieved using ultrasonic welding, maintaining the integrity and sterility of the products.
Surgical Instruments
- Plastic Components in Surgical Tools: Ultrasonic welding is used to join plastic parts in surgical instruments, providing reliable and durable connections that can withstand the rigors of surgical use.
Packaging Industry Applications
In the packaging industry, ultrasonic welding is used to seal plastic packaging materials without the risk of damaging the contents. The process provides a clean and reliable seal, making it ideal for various packaging applications.
Blister Packs
- Consumer Goods Packaging: Blister packs used for consumer goods, such as electronics and pharmaceuticals, are often sealed using ultrasonic welding, providing tamper-resistant and aesthetically pleasing packaging.
Tubes and Pouches
- Food and Beverage Packaging: Ultrasonic welding is used to seal plastic tubes and pouches in food and beverage packaging, ensuring a secure seal without compromising the contents.
Textile Industry Applications
Ultrasonic welding is also used in the textile industry, particularly for bonding synthetic fabrics. The process is faster and more efficient than traditional sewing methods and provides a strong, seamless bond.
Nonwoven Fabrics
- Disposable Hygiene Products: Ultrasonic welding is used to bond nonwoven fabrics in products like diapers, sanitary pads, and medical gowns, providing strong, clean seams without the need for stitching.
Synthetic Apparel
- Outdoor and Sportswear: Ultrasonic welding is used to bond synthetic materials in outdoor and sports apparel, creating waterproof and durable seams that are more comfortable than traditional sewn seams.
Comparison of Ultrasonic Welding with Other Joining Methods
To better understand the advantages of ultrasonic welding, it is useful to compare it with other common joining methods, such as heat welding, adhesive bonding, and mechanical fastening.
| Feature | Ultrasonic Welding | Heat Welding | Adhesive Bonding | Mechanical Fastening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Frictional heat from vibrations | External heat source | Chemical reaction | N/A |
| Materials Joined | Thermoplastics, some metals | Plastics, some metals | Plastics, metals, composites | All materials |
| Speed | Fast (seconds) | Slow to moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Need for Consumables | No | No (except for filler materials) | Yes (adhesives) | Yes (fasteners) |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate | Low to moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no emissions) | High (fumes, emissions) | Low to moderate | Low |
| Joint Strength | High | High | Moderate | High |
| Aesthetics | Clean, seamless joints | Potential for flash | May require cleanup | Visible fasteners |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, medical | Industrial, automotive | Packaging, general use | General use, construction |
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for various industrial applications.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Ultrasonic welding is a fast process, often completing in a few seconds, which increases productivity in manufacturing environments.
- Cost-Effective: By eliminating the need for additional materials such as adhesives or mechanical fasteners, ultrasonic welding reduces material costs and simplifies assembly.
- Strong and Reliable Bonds: The bonds created by ultrasonic welding are strong and can withstand mechanical stresses, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: The process does not produce harmful emissions, making it suitable for cleanroom environments and industries that prioritize sustainability.
- Flexibility: Ultrasonic welding can be used to join a wide range of materials, including dissimilar plastics and metals, which can be challenging for other welding methods.
Limitations of Ultrasonic Welding
Despite its many advantages, ultrasonic welding also has some limitations that need to be considered.
- Material Restrictions: Ultrasonic welding is most effective with thermoplastics and certain metals. Materials that do not conduct ultrasonic energy well may not be suitable for this process.
- Thickness Limitation: The process is generally limited to thinner materials, as thicker parts can absorb the vibrations, reducing the effectiveness of the weld.
- Initial Equipment Cost: The setup cost for ultrasonic welding equipment can be high, which may be a barrier for small-scale operations.
- Precision Requirement: The process requires precise control of welding parameters and alignment of parts, which can complicate the setup for complex geometries.
Future Trends in Ultrasonic Welding
As technology advances, ultrasonic welding continues to evolve with new innovations that expand its capabilities and applications.
- Automation and Robotics: The integration of ultrasonic welding with automated systems and robotics is increasing, allowing for fully automated production lines that enhance speed, consistency, and throughput.
- Advanced Materials: New horn designs and materials are being developed to expand the range of compatible materials, including advanced composites and high-performance plastics.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control: The use of sensors and advanced monitoring systems in ultrasonic welding allows for real-time feedback on the welding process, improving quality control and reducing defects.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding is a powerful and versatile joining method that offers significant advantages over traditional welding and assembly techniques. Its ability to create strong, reliable bonds quickly and without the need for additional materials makes it an invaluable tool in industries ranging from automotive and electronics to medical devices and packaging.
While the process does have some limitations, ongoing advancements in ultrasonic welding technology are likely to further enhance its performance and broaden its applications, making it an essential component of modern manufacturing.

I’m Darrell Julian, the founder, lead writer, and hands-on welding enthusiast behind ArcWeldingPro.com. With more than 15 years of real-world welding experience, I created this platform to share what I’ve learned in the field, in the shop, and in the heat of the arc.